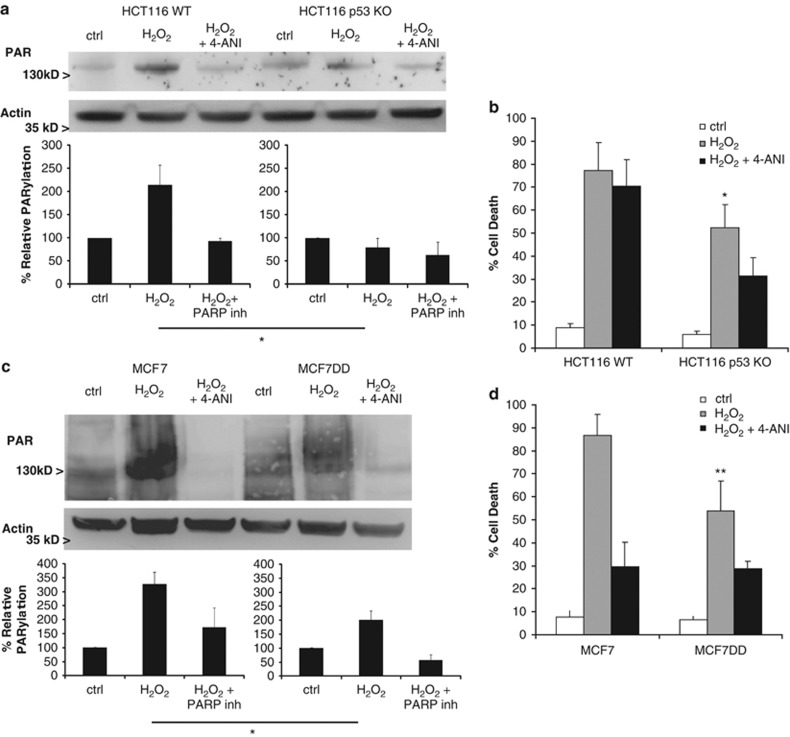
Figure 6.
p53 loss protects against PARP-mediated cell death in human colon carcinoma cells. (a) HCT 116 WT and p53 KO cells, and (b) WT MCF7 or p53 dominant-negative (DD) cells were treated for 1 h with 1 mM H2O2, with or without 4-ANI preincubation, and lysates (in the presence of PARG inhibitor ADP-HPD) were obtained and analyzed by western blot to detect protein-bound poly(ADP-ribose). Actin was used as loading control. (b and d) Cell death was analyzed at 24 h under the same treatments. Cells were stained with fluorescent conjugates of annexin-V and propidium iodide (PI) and analyzed by FACS. HCT116 p53 KO and MCF7 DD cells showed less PARylation compared with their respective WT, and were protected against H2O2-induced cell death. (a) and (c) belong to the same blot and immunodetection. Error bars indicate mean values±S.E.M. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 (compared with control cells for each cellular type). Densitometry analysis represent average±S.E.M. from at least three different western blots; results were normalized to untreated cells (ctrl) for each cellular type. All experiments were performed independently at least three times (N≥3)