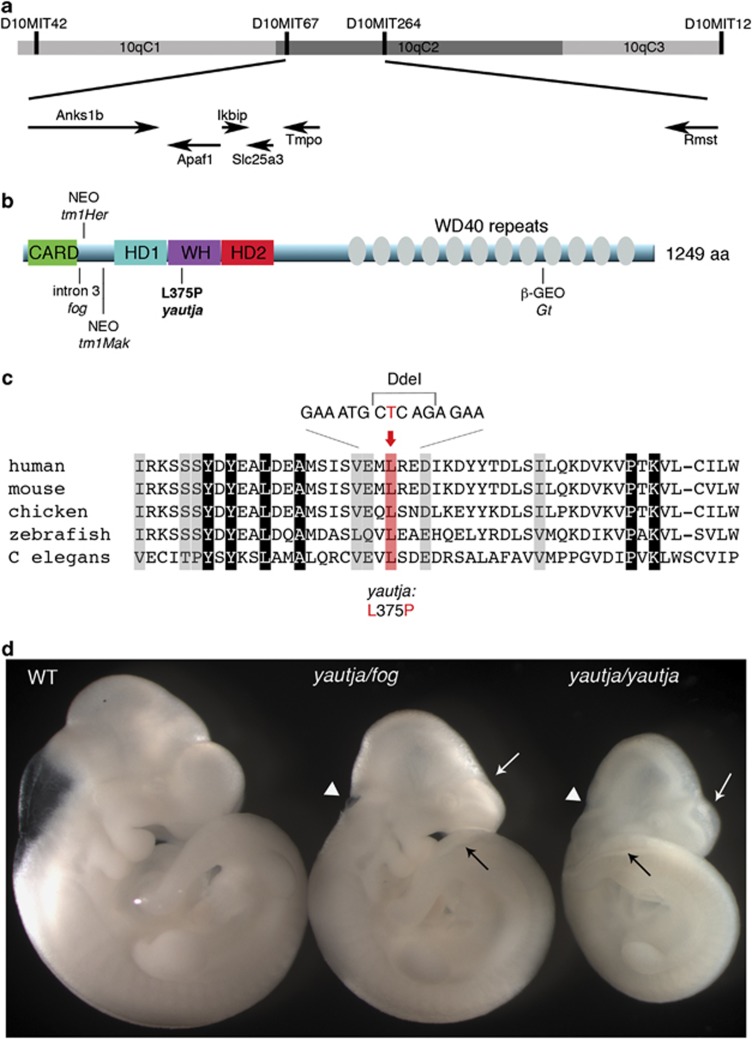
Figure 2.
Positional cloning of yautja identified a mutation in Apaf1. (a) Yautja was mapped to a 1.5-Mb interval bounded by markers D10MIT67 and D10MIT264 on chromosome 10. The arrows indicate the six genes in the interval and the direction of their transcription. (b) Schematic of the Apaf1 protein with domains indicated: caspase recruitment domain (CARD), helical domain I (HD1), winged-helix domain (WH), helical domain II (HD2) and multiple WD40-repeat domains. The existing Apaf1 mutant alleles are shown where they affect the protein: Apaf1fog inefficiently splices intron 3,22 Apaf1tm1Her has a neomycin cassette inserted at amino-acid 111,19 Apaf1tm1Mak inserted a neomycin cassette at exon 5,18 Apaf1yautja (L375P) is described in this paper and the Apaf1Gt has a gene trap insertion downstream of amino-acid 1018 (official symbol: Apaf1Gt(IRESBetageo)XIX18Pgr).20 (c) The yautja mutation changes a highly conserved leucine residue of Apaf1. Sequence comparison of a portion of the Apaf1 WHD showing evolutionary conservation; conserved residues are highlighted in gray. The red shading and text indicate the conserved leucine that is changed to proline by the yautja point mutation. Accession numbers used to produce the alignment were: human NP_863651, mouse NP_033814, chicken XP_416167, zebrafish NP_571683, Drosophila NP_7256347 and C. elegans NP_001021203. (d) The yautja mutation did not complement a functional null allele of Apaf1: Apaf1yautja/fog embryos share phenotypic features with Apaf1yautja and Apaf1fog: white arrow=flattened forebrain ventricles, black arrow=open caudal neural tube, white arrowhead=open rostral neural tube. Lateral view of E10.5 embryos