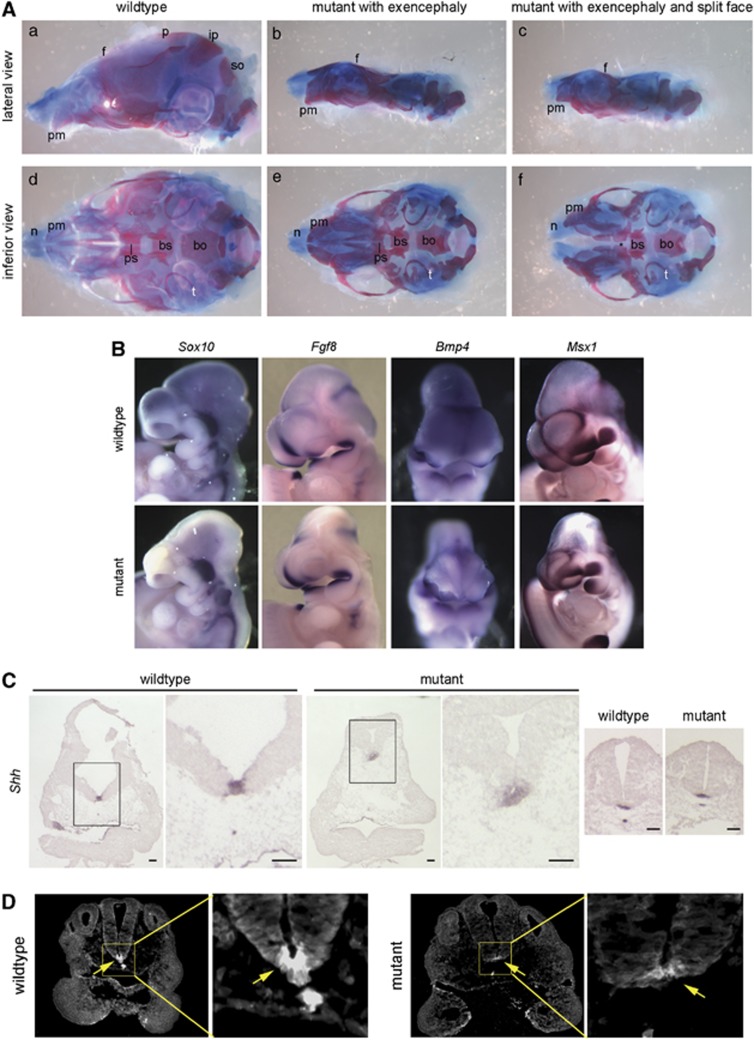
Figure 5.
Craniofacial defects: getting at a mechanism. (A) Preparations of P0 skulls from wild-type and yautja, stained with alcian blue and alizarin red. (b and c) In mutants with exencephaly, the frontal bone (f) is malformed and the parietal (p), interparietal (ip) and supraoccipital (so) bones are absent. (d–f) The inferior perspective allows visualization of skull base elements, including the tympanic rings (t), basisphenoid (bs), basioccipital (bo) and presphenoid (ps) bones. (f) A mutant with a split mid-face has widely spaced premaxillary bones (pm) and nasal cartilages (n), and also lacks the presphenoid bone (asterisk). (B) Expression of genes important during craniofacial development does not differ between wild-type and yautja. Whole-mount in-situ hybridization of E10.5 embryos with probes for Sox10, Fgf8, Bmp4 and Msx1. (C) Shh expression is expanded in the prechordal plate of yautja embryos. In-situ hybridization of E10.5 coronal sections through the head; the box in the first panel of each pair is enlarged in the second panel to show detail. Normal Shh expression is seen in the caudal neural tube floor plate and notochord of yautja mutants (last two panels). Scale bars=1 mm. (D) Shh protein is seen in a broader region of the prechordal plate of E9.5 yautja embryos. Anti-Shh immunofluorescence of horizontal sections at the level of the maxillary component of the first branchial arch; dorsal is to the top. The box in the first panel of each pair is enlarged in the second panel to show detail of the floor plate and Shh expression (arrows)