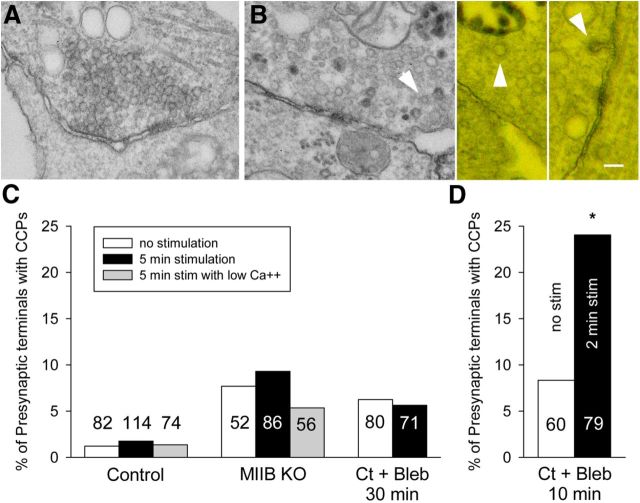
Figure 10.
The effect of stimulation on the frequency of presynaptic coated pits per synapse. A, An example of synapse for a culture that was treated with blebbistatin (50 μm) for a total of 10 min. Incubation with HRP was for 90 s without K+ stimulation. After a 30 s rinse with medium containing blebbistatin (to remove HRP) cells were fixed. B, Examples of synapses (two examples on right shown as anaglyphs) from cultures that were treated with blebbistatin for 10 min. Incubation with HRP was for 90 s during K+ depolarization. The 30 s rinse before fixation also contained blebbistatin and high K+. Coated pits (arrowheads) were frequently found in the presynaptic terminals. C, Comparison of the frequency of CCPs in presynaptic terminals of Ct (±blebbistatin) and MIIB KO cells unstimulated or following stimulation (K+ depolarization for 5 min). The number of synapses surveyed for each condition is indicated on the graph bars. The differences between the eight different categories are not significant (χ2 analysis, p = 0.13). The differences within groups are also not significant (Z-test). However, at t test comparing all three control values to all three MIIB KO values is significant (p = 0.007). In addition, a t test comparing controls to Ct + Bleb (no stimulation and 5 min stimulation) is also significant (p = 0.008). For low Ca2+, EGTA was used to buffer calcium to 200 nm. D, Comparison of CCPs in presynaptic terminals following a relatively short blebbistatin treatment (10 min) and a shorter K+ depolarization (2 min). Stimulation produced a significant (Z-test, *p = 0.028) increase in the frequency of CCPs. Scale bar, 100 nm.