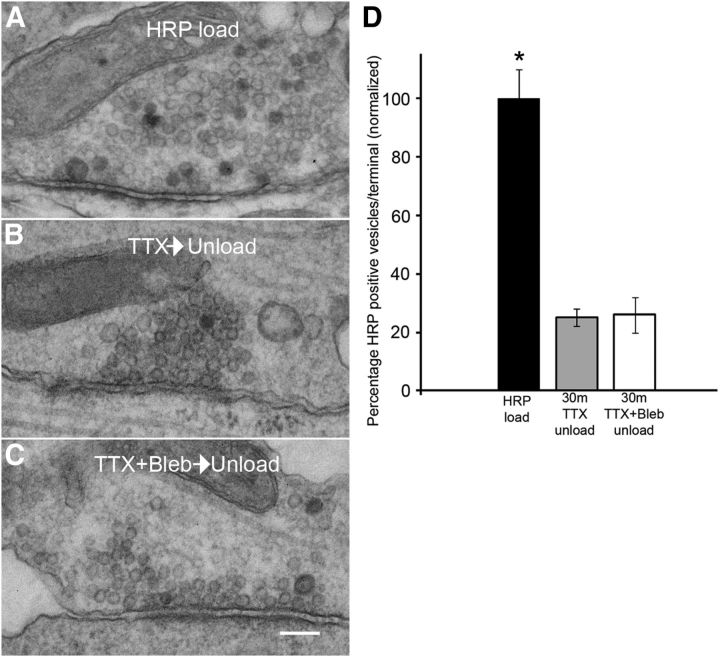
Figure 7.
Blebbistatin treatment does not inhibit release of HRP-positive vesicles. A, An example of a synapse from a Ct culture loaded with HRP using a 5 min K+ depolarization and then incubated with TTX for 30 min before fixation (no second depolarization). Ninety-six percent of synapses had HRP-positive synaptic vesicles. B, An example of a synapse from a Ct culture loaded with HRP using a 5 min K+ depolarization and then incubated with TTX for 30 min before a second K+ depolarization (2 min) and fixation. Seventy-nine percent of synapses had HRP-positive vesicles. C, An example of a synapse from a Ct culture loaded with HRP using a 5 min K+ depolarization then incubated with TTX + blebbistatin (50 μm) for 30 min before a second depolarization (2 min) in the presence of blebbistatin and then fixation. Sixty-six percent of synapses had HRP-positive synaptic vesicles. Scale bar, 130 nm. D, Quantitative analysis of synaptic terminals treated as indicated in A–C. Blebbistatin does not prevent unloading of HRP-positive vesicles. Difference between groups was significant, ANOVA, p < 0.0001; Ct (HRP load), N = 26 synapses from two circuits; 30 min TTX then unload, N = 44 synapses from three circuits; Blebbistatin treated (30 min TTX + Bleb and then unload) N = 46 synapses from 3 circuits. * Differences were significant (ANOVA, p < 0.0001). Difference between TTX and TTX + Bleb unload was not significant, t test, p = 0.8. Error bars indicate SEM.