Figure 2.
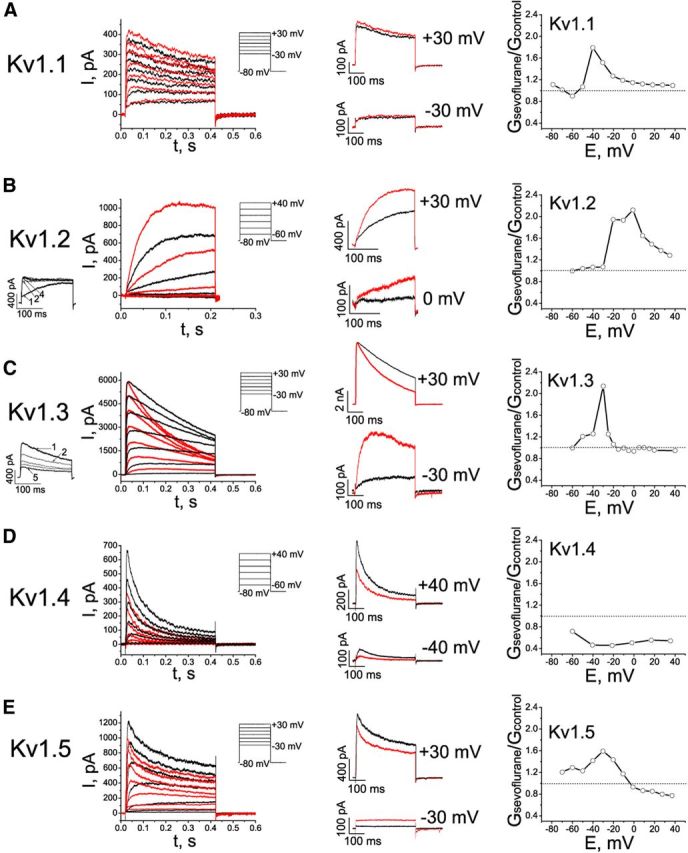
Effects of sevoflurane on potassium currents in cells expressing mammalian Kv1 channels. A–E, Left, Representative outward currents evoked by depolarizing pulses from a holding potential of −80 mV to the range of potentials from −30 to +30 mV, with 10 mV increments and interpulse intervals of 10 s for recording Kv1.1 currents or 30 s for recording Kv1.2, Kv1.3, Kv1.4, and Kv1.5 currents. Control (black) currents are superimposed with currents recorded in the presence of 0.2 mm sevoflurane (red). The cells were exposed to aqueous anesthetic solutions prepared as described previously (Mandal and Pettegrew, 2008). Middle, Comparison of the sevoflurane effects on outward potassium currents at low and higher membrane potentials. The traces shown are the same as in left panels, only scaled as indicated. Right, Voltage dependence of the sevoflurane-mediated conductance changes (n = 3–9 cells).
