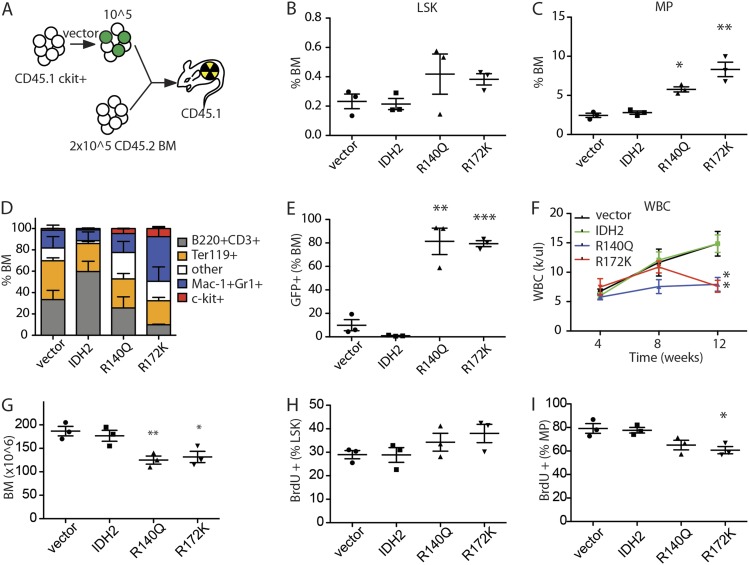
Figure 4.
IDH2 mutations are sufficient to block differentiation of HSPCs and alter DNA methylation. (A) Schematic diagram of competitive transplant assay. Vector refers to transduction of cells with empty MSCV-IRES-GFP vector or one coexpressing wild-type IDH2 or an IDH2 mutant. CD45.1 c-kit+ HSPCs (105) transduced with vectors were mixed with 2 × 105 CD45.2 BM and transplanted into lethally irradiated CD45.1 recipient mice. (B) Percentage of lin−Sca-1+c-kit+ (LSK) cells in the whole BM of recipient mice 12 wk after transplantation. n = 3. (C) Percentage of lin−Sca-1−c-kit+ (MP) cells in the whole BM of recipient mice 12 wk after transplantation. n = 3. (D) Percentage of c-kit+, Mac-1+ or Gr-1+, B220+ or CD3+, and Ter119+ cells in the whole BM of recipient mice 12 wk after transplantation. n = 3. (E) Percentage of GFP+ cells in the whole BM of recipient mice 12 wk after transplantation. n = 3. (F) WBC counts of recipient mice with IDH2 wild-type- or mutant-expressing cells. n = 4–5. (G) BM cellularities of recipient mice with IDH2 wild-type- or mutant-expressing cells at 12 wk after transplantation. n = 3. (H) BrdU incorporation rate of LSK cells after 1 d of labeling. n = 3. (I) BrdU incorporation rate of MP cells after 1 d of labeling. n = 3. Of note, in B–G, vector, IDH2, or IDH2 mutants refers to mice transplanted with HSPCs transduced with the indicated vector but does not necessarily indicate that all of the cells analyzed expressed the constructs. Specifically, while BM from mice transplanted with IDH2 mutant cells almost completely consisted of GFP+ IDH mutant-expressing cells (shown in E), empty vector and wild-type IDH produced a competitive disadvantage, and BM consisted entirely of GFP− normal competitors at this time point.