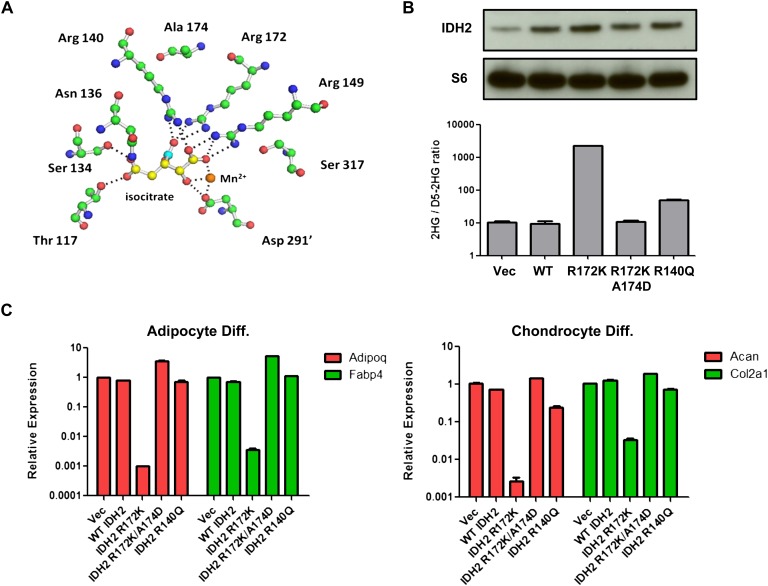
Figure 4.
Differentiation impairment by mutant IDH2 correlates with 2HG production. (A) Structural modeling of IDH2 catalytic site showing Arg 172 and Ala 174. Isocitrate carbons are in yellow except carbon 6 containing the β-carboxyl, which is highlighted in cyan. Carbon atoms of amino acids (green), amines (blue), and oxygens (red) are also depicted. Hydrogen atoms are omitted for clarity. Dashed lines show <3.1 Å interactions corresponding to hydrogen and ionic bonds. The prime (′) denotes that the residue comes from the other monomer of the IDH dimer. (B) 10T cells expressing vector (Vec), wild-type (WT), R172K, R172K/A174D, or R140Q mutant IDH2 were lysed, and IDH2 expression was measured by Western blot. 2HG levels were measured by GC-MS and normalized to internal standard (D5-2HG) and cell number. (C) 10T cells expressing wild-type or various mutant IDH2 were treated with adipocyte or chondrocyte differentiation cocktails. mRNA expression of Adipoq, Fabp4, Acan, and Col2a1 was measured by qRT-PCR after 8 d of differentiation induction. For all experiments, the average ± SD from three biological replicates are shown.