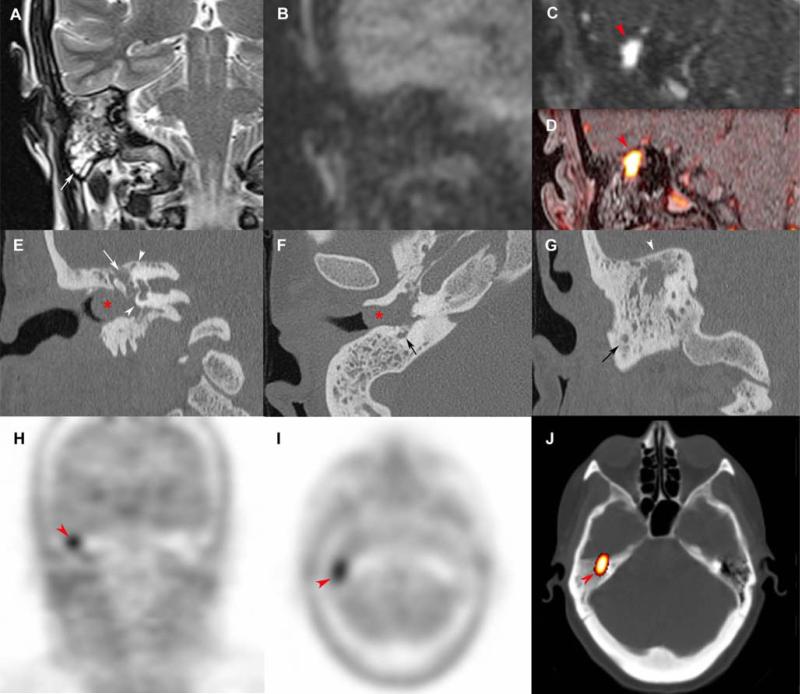
Figure 3. Tympanic paraganglioma in a rare attical location.
Coronal SE T2-weighted (A), non-EPI-b1000-DWI (B), early arterial 4D Dynamic MR Angiography (MRA) (C), fat-saturated (FATSAT) T1-weighted/4D-MRA fusion image (D), CT reconstructions with a bone algorithm (E, F, G), coronal 18F-FDOPA PET (H), axial 18F-FDOPA PET (I), and axial 18F-FDOPA PET/CT fusion image (J).
Chronic otitis media with full field tympanic cavity (A, white arrow) associated with an 8 mm inflammatory polyp in the external auditory canal (E, F, red asterix). Absence of cholestatoma on non-EPI-b1000-DWI (B). MRI shows a 7 mm attic paraganglioma, located in the superior and medial side of the uncudo-mallear joint, with a typical hyper-vascularization pattern (C, D, red arrowhead). CT reconstructions were useful in the preoperative evaluation of the tegmen tympani's integrity (G, white arrowhead), the facial nerve canal (E: white arrows, F: black arrow), and the otic capsule (E, arrow heads). The tumor was highly avid for 18F-FDOPA.