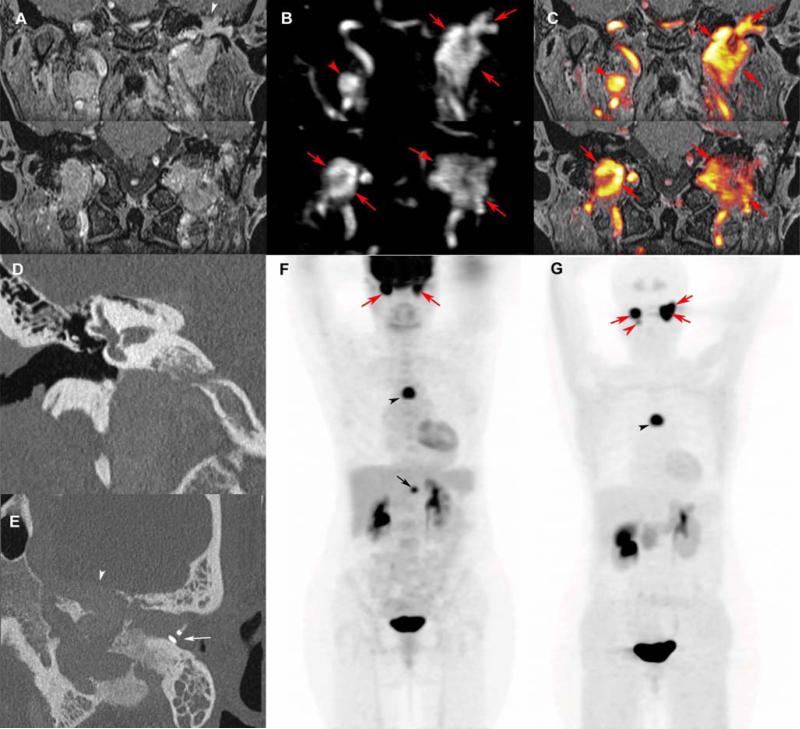
Figure 7. Multifocal and recurrent SDHD-related extra-adrenal PGLs.
Coronal 3D volumetric interpolated fat-saturated (FATSAT) T1-weighted (VIBE) (A), early arterial 4D Dynamic MR Angiography (B), FATSAT T1-weighted/4D-MRA 3D fusion image (C), coronal CT bone reconstruction of the right (D) and axial oblique CT bone reconstruction of the left ear (E), 18F-FDG PET (MIP) (F), and 18F-FDOPA PET (MIP) (G).
MRI with 4D Dynamic MR angiography shows bilateral jugular PGL (red arrows), spreading in the tympanic cavity on the left side, and a right vagal PGL (red arrowheads). CT shows bilateral enlargement of the jugular foramens and sugar bone erosions (D, E). The left tegmen tympani and the anterior wall of the attic are widely eroded by jugulo-tympanic PGL (A, E, white arrowhead). The tumor mass effect is responsible for a complete prosthetic luxation (E, white arrow), explaining the recurrent left conductive hearing loss. 18F-FDG and 18F-FDOPA PE/CT also reveal a mediastinal parasympathetic PGL (F, G, black arrowheads). In comparison to 18F-FDG PET/CT, 18F-FDOPA PET missed an abdominal paraaortic PGL (F, black arrow) and detected one more HNPGL (left vagal PGL, G: red arrowhead). False negative sympathetic PGL on 18F-FDOPA PET is not uncommon in SDHx-related PGL syndromes.