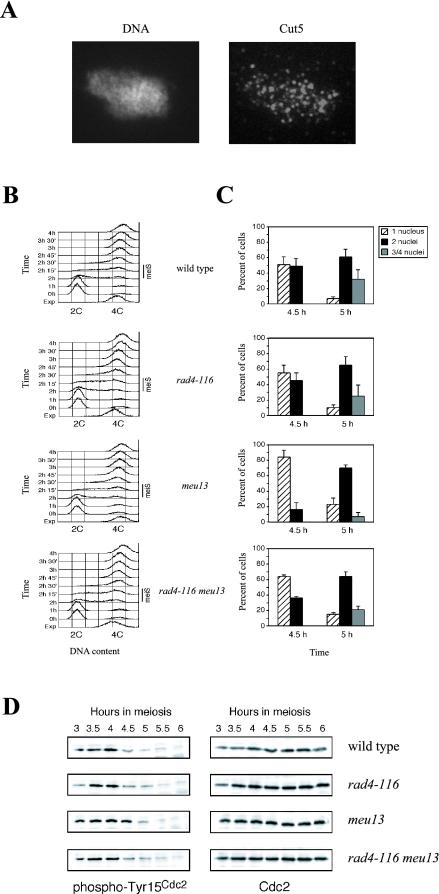
Figure 6.
The S. pombe Cut5/Rad4 protein is required for the meiotic recombination checkpoint. (A) Spread nuclei of S. pombe strain S964 (wild type) prepared after 3 h of induction of the meiotic program (corresponding to meiotic prophase I; see Perez-Hidalgo et al., 2003) stained with DAPI (left) and anti-Cut5 antibody (right). (B) Flow cytometry analysis of DNA content during pat1-induced synchronous meiosis at 32°C of strains S964 (wild type; top panel), S1329 (rad4-116; second panel from the top), S1295 (meu13; second panel from the bottom), and S1330 (rad4-116 meu13; bottom panel). Note that the timing of premeiotic DNA replication (meiS) is the same in all strains. A representative experiment is shown, but it has been repeated three times obtaining similar results. (C) The rad4-116 mutation abolishes a checkpoint-dependent delay of entry into meiosis I. Kinetics of meiotic progression at 32°C of strains S964 (wild type; top panel), S1329 (rad4-116; second panel from the top), S1295 (meu13; second panel from the bottom) and S1330 (rad4-116 meu13; bottom panel) was followed by DAPI staining of nuclei. The whole time course of meiosis (from 0 to 9 h) was analyzed (unpublished data; see Perez-Hidalgo et al., 2003 for details) but, for clarity, only the data corresponding to the relevant time points (4.5 and 5 h) representing the onset of the first meiotic division are presented. The percent of uninucleated cells (striped bars) that have not yet undergone meiosis I, binucleated cells (black bars) that have undergone meiosis I, and tri- or tetranucleated cells (gray bars) that have undergone meiosis II is shown. The average values (including SD) of three independent experiments are presented. At least 400 cells were scored for each strain at every time point in each experiment. (D) The Cut5-dependent meiotic recombination checkpoint regulates phosphorylation of Cdc2 on tyrosine 15. Western blot analysis of meiotic time courses of strains S964 (wild type), S1329 (rad4-116), S1295 (meu13), and S1330 (rad4-116 meu13), using antiphospho-Cdc2(Tyr15) and anti-Cdc2 antibodies. Note that phosphorylation of Cdc2 on Tyr15 persists longer in the meu13 mutant compared with the rad4-116 meu13 double mutant (see the 4.5-h time point).