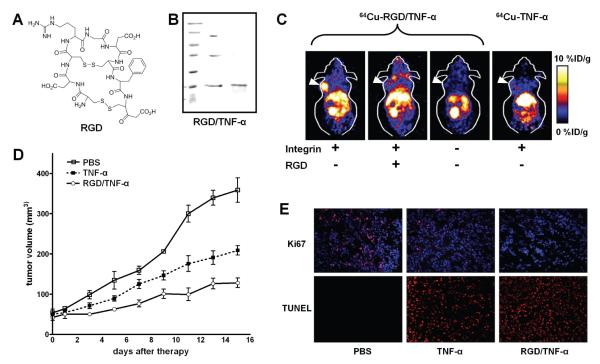
Figure 3.
Evaluation of a RGD/TNF-α fusion protein for targeted cancer therapy. A. The chemical structure of the RGD peptide used for tumor integrin αvβ3 targeting. B. Gel electrophoresis of the RGD/TNF-α fusion protein. Under non-reducing condition, the fusion protein runs as monomer, dimer, and trimer (middle lane). Under reducing condition, the fusion protein runs as a monomer (right lane). C. Non-invasive PET imaging demonstrated integrin αvβ3 specific tumor uptake of 64Cu-labeled RGD/TNF-α but not TNF-α. Decay-corrected coronal slices of tumor-bearing mice (arrowheads) at 4 h post-injection are shown. D. RGD/TNF-α caused statistically significant tumor growth inhibition comparedd to either TNF-α or PBS treated control. E. Immunofluorescence staining of the frozen tumor sections confirmed the anti-cancer effects observed in vivo. The fluorescence signal is colored coded red and the blue dots represent the nuclei. Adapted from (Wang et al. 2008).