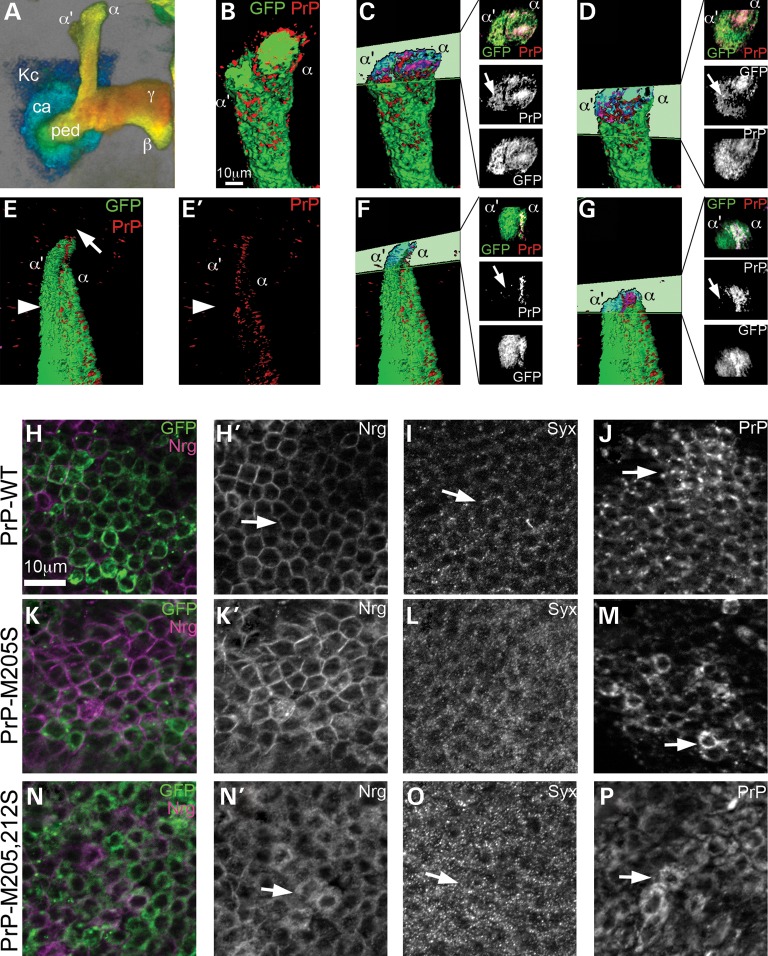
Figure 7.
PrP-M205,212S induces the abnormal distribution of other membrane proteins. (A) 3D image of mushroom body neurons, color-coded for depth: posterior in blue, anterior in red. Kc, Kenyon cells; ca: calix, ped: pedunculus, α, β, γ: projections. (B–G) 3D surface visualization of PrP distribution in mushroom body dorsal projections. (B) PrP-WT colocalizes with GFP throughout the mushroom body projections. (C and D) Cross-sections through the dorsal lobes show co-distribution of PrP and GFP in α and α′ (arrow) branches. (E and E′) PrP-M205,212S does not form the cap (arrow), and PrP is not present in the α′ axons labeled with GFP (arrowhead). (F and G) Cross-sections show a lack of PrPs in the α′ branch (arrows). (H–M′) PrP-M205,212S disrupts the distribution of Syx and Nrg in cell bodies. (H and H′) PrP-WT accumulates in the Golgi and the membrane in Kc (arrow). (I and I′) PrP-M205,212S accumulates in small vesicles in the Kc (arrow). In flies expressing PrP-WT, Syx displays low levels of Syx in the Kc (J and J′, arrow) and Nrg accumulates in the membrane (L and L′, arrow). In contrast, flies expressing PrP-M205,212S, accumulates higher levels of Syx (K and K′, arrow) and dissociation of Nrg from the membrane (M and M′, arrow).