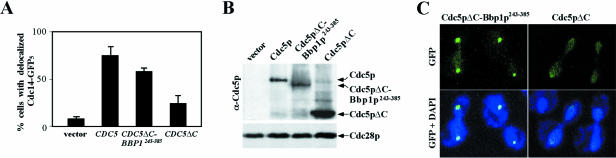
Figure 8.
Cdc5pΔC-Bbp1p243–385 can induce the Cdc14p release from the nucleolus. (A) Strain SAY801 (Cdc14p-GFP5) integrated with GAL1 vector (pCJ238), GAL1-CDC5 (pCJ241), GAL1-CDC5ΔC-BBP1243–385 (pCJ240), or GAL1-CDC5ΔC (pCJ242) was cultured in YEP-raffinose overnight and then transferred to YEP-galactose medium containing 15 μg/ml of nocodazole for 2.5 h before fixation with formaldehyde to assess the subcellular localization of Cdc14p-GFP5 by GFP fluorescence. The percentages of cells with Cdc14p-GFP5 at the nucleolus were determined by counting >200 cells for each sample. Data were obtained from three independent experiments. Error bars indicate SD. Vector, strain KLY4079; CDC5, strain KLY4085; CDC5ΔC-BBP1243–385, strain KLY4091; and CDC5ΔC, strain KLY4096. (B) Expression levels of the above constructs were examined after transforming each plasmid into the protease-negative JB811 strain. Total cellular protein prepared from each transformant was subjected to immunoblotting with an anti-Cdc5p antibody. The levels of Cdc28p are shown as loading controls. (C) To determine the localization of Cdc5pΔC-Bbp1p243–385 or Cdc5pΔC, strain KLY1546 transformed with GAL10-YFP-CDC5ΔC-BBP1243–385 (pKL2071) or GAL10-YFP-CDC5ΔC (pCJ231) was cultured under induction conditions for 2.5 h, fixed, and then subjected to fluorescent microscopy.