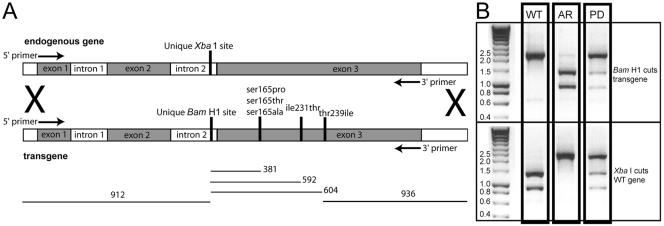
Figure 2.
(A) Diagram of the exon-intron structure of α-tubulin. Endogenous (wild-type) α-tubulin has a unique XbaI restriction site in intron 2. The transgene was altered to ablate the XbaI site and to introduce a unique BamHI site in intron 2. The point mutations Ser165Pro, Ser165Thr, Ser165Ala, Ile231Thr, and Thr239Ile were introduced in the transgene construct both individually and in double and triple combinations. The α-tubulin from transformants with oryzalin resistance was amplified with primers (arrows) that are internal to the 5′ and 3′ ends of the transgene and represent the 5′ end of exon 1 and 3′ end of exon 3. (B) Restriction enzyme analysis of the transformed oryzalin-resistant lines gives easily distinguishable patterns after amplification of the α-tubulin gene. The endogenous (WT) α-tubulin gene is cut by BamH1 and is not cut by XbaI. Conversely, the allelic replacement (AR, homologous integration) is cut by XbaI and is not cut by BamHI. Nonhomologous integration of the transgene creates a pseudodiploid (PD). In this case, both the BamHI and XbaI enzymes cut incompletely.