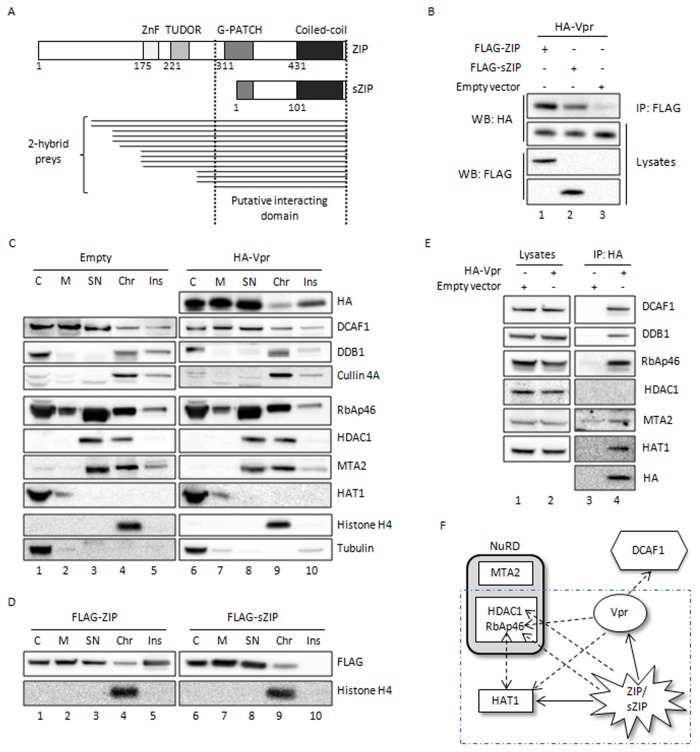
Figure 1. Interaction of HIV-1 Vpr with ZIP and sZIP and with the NuRD complex.
A. Schema of ZIP and sZIP and Vpr-interacting fragments. Vpr was used as bait in a yeast two-hybrid screen of oligo d(T)-primed cDNAs from human CEMC7 cells. ZIP and sZIP isoforms are represented by boxes, with their known domains in different shades of grey. The preys matching with ZIP are drawn as thin lines below the diagram representing ZIP and sZIP proteins. B. Vpr interacts with both ZIP and sZIP in HEK293T cells. HEK293T cells were transfected with vectors expressing HA-tagged Vpr and the indicated FLAG-tagged proteins. Cell lysates were prepared 48h post-transfection and subjected to immunoprecipitation using anti-FLAG antibodies. After extensive washing, bound proteins were eluted from beads with a FLAG peptide. Immunoprecipitates (IP) and crude cell lysates (Lysates) were analyzed by Western blotting using the indicated antibodies. C. Chromatin is the only fraction where Vpr, Cul4ADDB1 and members of the Mi-2/NuRD complex (RbAp46, HDAC1 and MTA2) are detected together. HeLa cells were transfected with either a vector expressing HA-tagged Vpr or an empty vector. Cells were harvested 48h post-transfection and subcellular fractionation was performed on 2 106 cells to obtain cytoplasmic (C), membrane (M), nuclear soluble (SN), chromatin-bound (Chr) and insoluble (Ins) protein extracts. The final volume ratio of each fraction is 2:2:1:1:1 respectively. The cellular distribution of the Vpr protein was analyzed by Western blot, as well as the cellular distribution of the indicated endogenous proteins. D. ZIP and sZIP are detected in the chromatin fraction. HeLa cells were transfected with vector expressing either FLAG-ZIP or FLAG-sZIP. Cells were harvested 48h post-transfection and subcellular fractionation was performed in the same conditions as described above. E. Vpr recruits RbAp46 and HAT1 in HEK293T cells. HEK293T cells were transfected with either a vector expressing HA-tagged Vpr or an empty vector. Cell lysates were prepared 48 h post-transfection and subjected to immunoprecipitation using anti-HA antibodies. Immunoprecipitates (IP) and crude cell lysates (Lysates) were analyzed by Western blotting using the indicated antibodies. F. Interactions detected between Vpr, ZIP/sZIP and the Mi-2/NuRD complex. Interactions detected by co-immunoprecipitation are represented on this diagram. The direction of the arrow indicates the direction of the co-immunoprecipitation (base of the arrow: immunoprecipitated protein, arrow: co-immunoprecipitated protein). Full arrows correspond to new interactions we have unraveled here and arrows in dotted line interactions previously described and confirmed in this study [32,33,38]. Interactions between ZIP/sZIP and HAT1, RbAp46 and HDAC1 are shown in Figure S2.