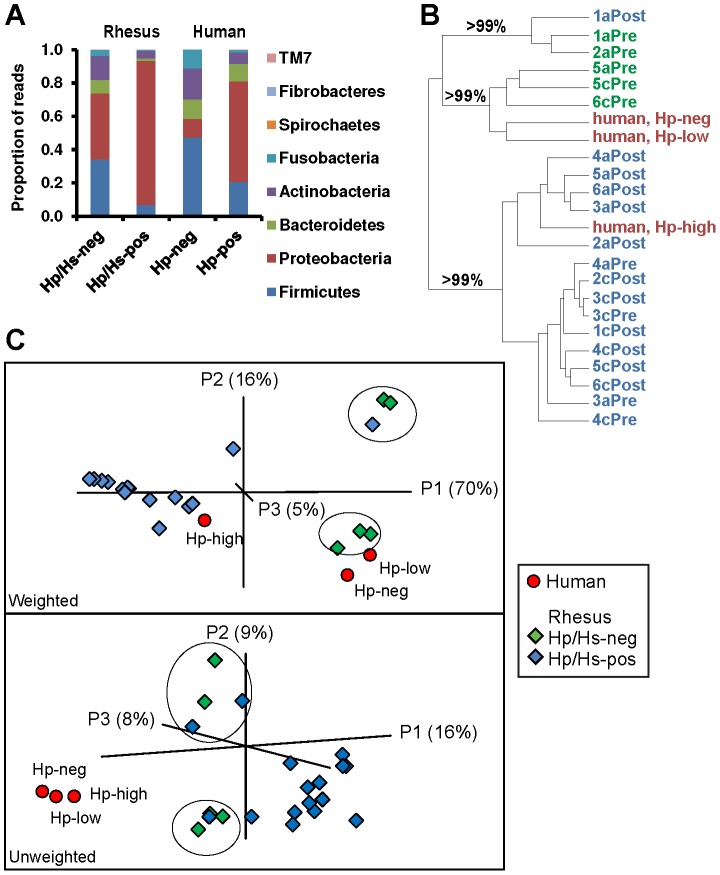
Figure 3. Community structure of rhesus macaque and human gastric communities in the presence (pos) or absence (neg) of H. pylori (Hp) or H. suis (Hs).
(A) Phylum-level profiles of the microbiota of the rhesus monkey and human stomach. (B and C) Cluster analysis of UniFrac distances between communities. Text and shape color indicate human samples (red) and the Helicobacter status of rhesus macaque samples (green, negative; blue; positive). (B) Jackknife analysis was performed for H. pylori-negative (Pre) or H. pylori-positive (Post) libraries from the antrum (a) or corpus (c) of each subject (m 1–6), as well as human libraries that have negative, low, or high H. pylori status. Cluster recovery is indicated at key branch points. (C) Principal Coordinates Analysis (PCoA) of abundance weighted (top panel) or unweighted (bottom panel) UniFrac distances demonstrated clustering by relative abundance of H. pylori and between co-housed animals. Circles enclose Helicobacter-negative or -low libraries from pair mates m 1, 2 and m 5, 6.