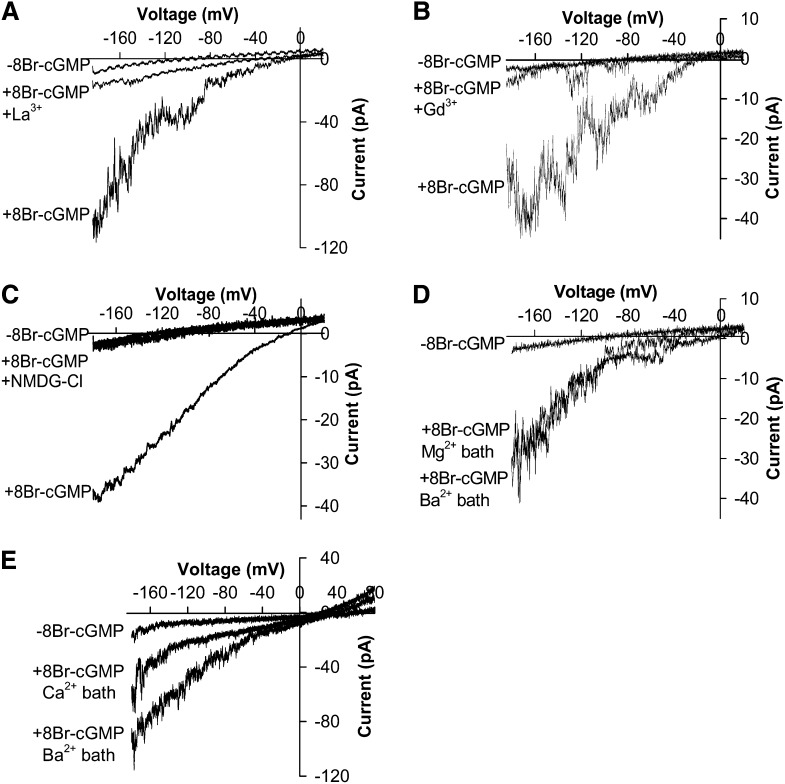
Figure 2.
Ion selectivity and blocker sensitivity of 500 μm 8Br-cGMP-activated channels recorded in Arabidopsis Columbia wild-type guard cell protoplasts. A, Whole-cell recording in a Columbia wild-type guard cell protoplast showing the inhibition of 8Br-cGMP (500 μm)-activated currents by the Ca2+ channel blocker La3+ (100 μm). B, Whole-cell recordings in a Columbia wild-type guard cell protoplast showing 8Br-cGMP-activated channel inhibition by the Ca2+ channel blocker Gd3+ (100 μm). Two overlapping traces after Gd3+ application are depicted. C, Whole-cell recording of a Columbia wild-type guard cell protoplast showing the inhibition of 8Br-cGMP-activated currents by the replacement of Mg2+ in the bath solution by 100 mm NMDG-Cl. Two overlapping traces before 8Br-cGMP application and after replacement of Mg2+ in the bath solution by 100 mm NMDG-Cl are depicted. D, Whole-cell recording of 8Br-cGMP-activated currents in a Columbia wild-type guard cell protoplast showing similar current amplitudes when MgGlu and MgCl2 in the bath solution were replaced with 100 mm BaCl2. E, 8Br-cGMP-activated currents in a Columbia wild-type protoplast recorded using BaCl2 pipette and bath solutions without NADPH in the pipette solution (see “Materials and Methods”). 8Br-cGMP-activated currents were recorded in a 100 mm BaCl2 bath solution first, and then 100 mm BaCl2 in the bath solution was replaced with 100 mm CaCl2.