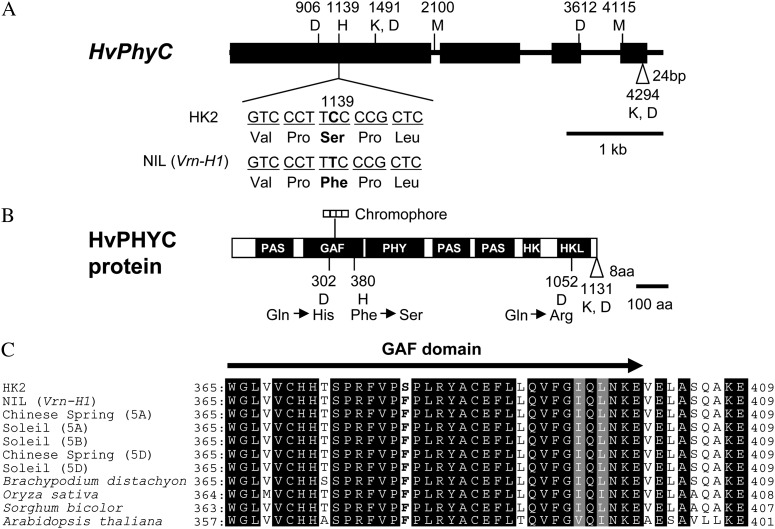
Figure 2.
Structure of HvPhyC gene and its protein. A, HvPhyC gene sequences from HK2 and NIL (Vrn-H1) were compared with those from var. Morex (DQ238106), var. Dicktoo (DQ201145), and var. Kompolti Korai (DQ201146). Black boxes and horizontal lines between them indicate exons and introns, respectively. Vertical line indicates SNP when NIL (Vrn-H1) was compared with other varieties. White triangle indicates a 24-bp insertion. NIL (Vrn-H1), HK2, and Morex have this insertion, which results in an 8-amino acid insertion. Numbers and letters at polymorphic sites indicate the position and polymorphic varieties, respectively. H, M, D, and K indicate HK2, Morex, Dicktoo, and Kompolti Korai, respectively. B, Deduced amino acid sequences were compared based on the HvPhyC gene sequences. Black boxes indicate domains. Polymorphisms are shown in the same way as HvPhyC gene. HK, His kinase domain; HKL, His kinase-like ATPase domain. C, Deduced amino acid sequences around the C-terminal end of GAF domain were compared based on the genomic sequences of barley, wheat (GenBank: AY672995.1, AY673002.1, AY672998.1, AY672999.1, and AY673000.1), B. distachyon (Gbrowse: Bradi1g08400.1), rice (RAP-DB: Os03g0752100-01), and sorghum (GDB: Sb01g007850.1). The same and similar sequences are highlighted in black and gray, respectively.