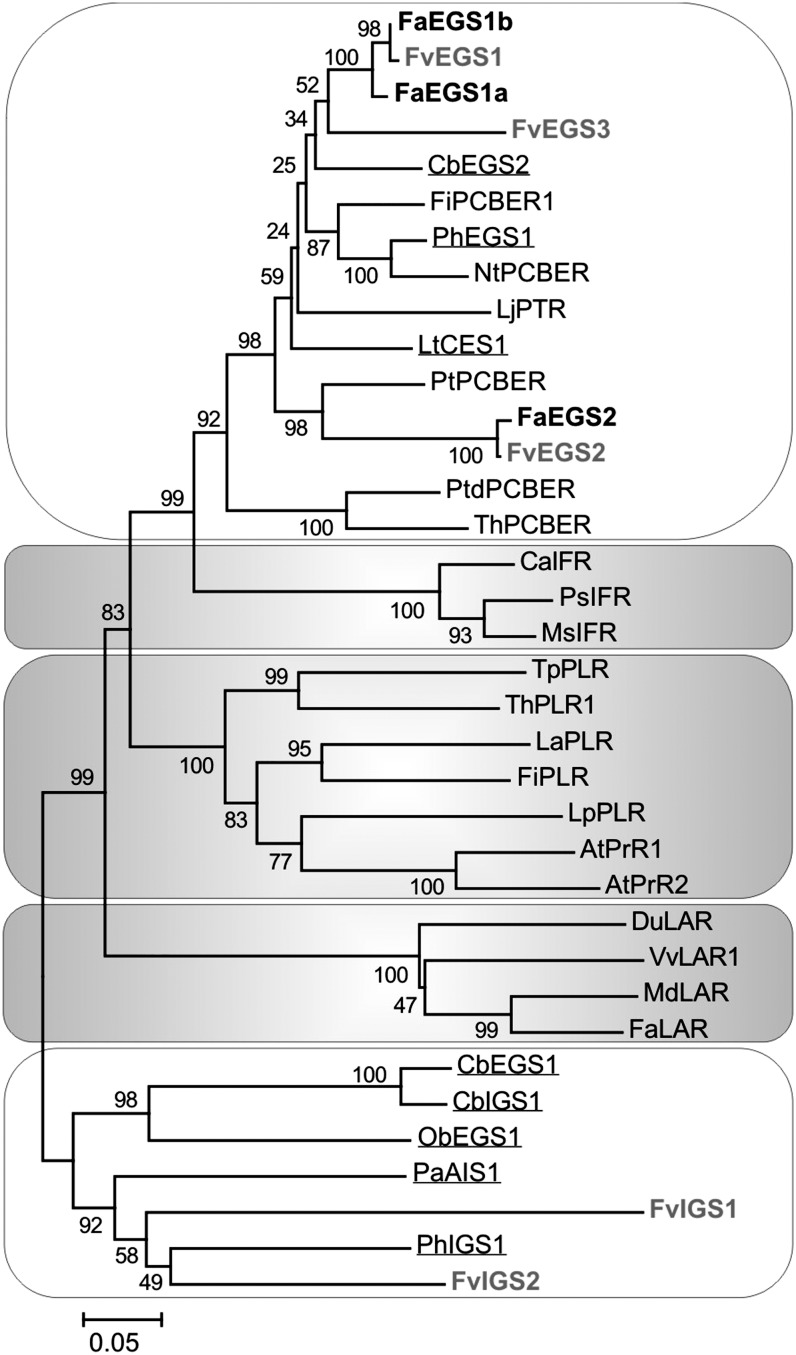
Figure 2.
Unrooted phylogenetic tree of selected protein sequences in the PIP family of NADPH-dependent reductases, including FaEGS1a, FaEGS1b, and FaEGS2, as well as putative FvEGSs and FvIGSs. The two clades in which eugenol- and isoeugenol-forming enzymes are grouped are shown with a white background. The different clades of isoflavone reductases (IFRs), pinoresinol lariciresinol reductases (PLRs) together with pinoresinol reductases (PrRs), and leucoanthocyanidin reductases (LARs) are shown with a gray background. FaEGSs (black) and F. vesca putative EGSs and IGSs (gray) are shown in boldface. The proteins with EGS or IGS activity characterized in C. breweri, O. basilicum, P. × hybrida, P. anisum, and L. tridentata are underlined. Sequence analysis was performed by using ClustalW, and the neighbor-joining method was used to generate the tree. The percentages of replicate trees in which the associated proteins clustered together in the bootstrap test (1,000 trials) are shown next to the branches. The evolutionary distances were computed by using the p-distance method (this distance is the proportion, p, of amino acid sites at which the two sequences to be compared are different), and the scale is in units of the number of amino acid differences per site. Evolutionary analyses were conducted in MEGA5 (Tamura et al., 2011). The accession numbers corresponding to the sequence data used in this study are listed in Supplemental Table S1. Cb, Clarkia breweri; Fi, Forsythia × intermedia; Nt, Nicotiana tabacum; Lj, Lotus japonicus; Lt, Larrea tridentata; Pt, Populus trichocarpa; Ptd, Pinus taeda; Th, Tsuga heterophylla; Ca, Cicer arietinum; Ps, Pisum sativum; Ms, Medicago sativa; Tp, Thuja plicata; La, Linum album; Lp, Linum perenne; At, Arabidopsis thaliana; Du, Desmodium uncinatum; Vv, Vitis vinifera; Md, Malus × domestica; Pa, Pimpinella anisum.