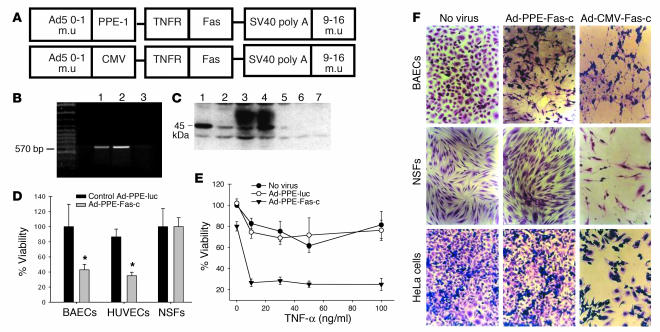
Figure 2.
Construction and activity of PPE-directed Fas-c recombinant adenoviruses. (A) Schematic representation of the recombinant adenovirus early region 1–deleted (E1-deleted) vectors. m.u, map units; simian virus 40 (SV40 poly A). (B) RT-PCR analysis of BAECs infected by Ad-PPE-Fas-c. Lane 1: Fas-c plasmid, positive control. Lane 2: Ad-PPE-Fas-c virus. Lane 3: Ad-PPE-luc virus, negative control. (C) Western blot analysis of BAECs infected with Ad-PPE-Fas-c. Lanes 1 and 2: BAECs transfected with pcDNA3-Fas-c (positive control). Lanes 3 and 4: BAECs infected with Ad-PPE-Fas-c at MOI 100 and 1,000, respectively. Lane 5: Noninfected BAECs. Lanes 6 and 7: BAECs infected with Ad-PPE-luc at MOI 100 and 1,000, respectively. (D) Crystal violet viability assay of endothelial cells (BAECs and HUVECs) and nonendothelial cells (NSFs) infected with Ad-PPE-Fas-c at MOI 1,000. Cells were infected with Ad-PPE-Fas-c or Ad-PPE-luc or were not infected. Each bar represents the mean ± SD of four to six replicates of six to eight wells. *P < 0.05 vs. control vector–infected cells. (E) Sensitization of ECs to TNF-α cytotoxicity by Ad-PPE-Fas-c infection. BAECs were infected with Ad-PPE-Fas-c or control virus. Human TNF-α at the indicated concentrations was added to the culture media. (F) The effect of Ad-CMV-Fas-c on apoptosis in ECs and nonendothelial cells. BAECs, NSFs, and HeLa cells were infected with Ad-PPE-Fas-c (center) or Ad-CMV-Fas-c (right) at MOI 1,000 and stained by crystal violet. Nonendothelial cells were unaffected by Ad-PPE-Fas-c; however, massive apoptosis was induced by Ad-CMV-Fas-c infection. ×200.