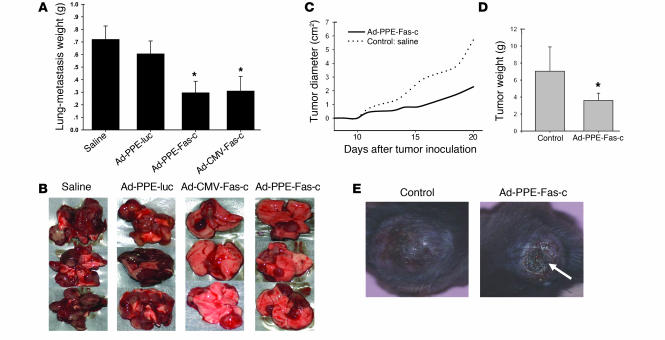
Figure 4.
Systemic administration of Ad-PPE-Fas-c inhibited tumor growth. (A) LLC lung metastases were created in male mice. Ad-PPE-Fas-c, Ad-CMV-Fas-c, Ad-PPE-luc, or saline was injected i.v. into the tail vein. Weight due to tumor burden was calculated by subtraction of the average normal wet organ weight (200 mg) from each tumor-bearing organ. Each bar represents the mean ± SE, n = 14–16. *P < 0.05 vs. control groups. (B) Representative lung surfaces of treated versus untreated mice. (C) Tumor growth kinetics. Male C57BL/6J mice were inoculated subcutaneously on the hind flank with 7.5 × 106 B16 melanoma cells. Saline (n = 4) or Ad-PPE-Fas-c (n = 7) was injected i.v. when tumor was palpable. Tumor diameter was calculated from tumor measurements scored at the indicated postimplantation day. The growth of B16 melanoma was significantly inhibited in mice treated with Ad-PPE-Fas-c compared with control mice. (D) B16 melanoma tumor weights at the day of sacrifice. Tumor weights were lower in mice injected with Ad-PPE-Fas-c. *P < 0.05 vs. control group. (E) Prominent tumor necrosis in an Ad-PPE-Fas-c–treated mouse. Arrow: necrotic area.