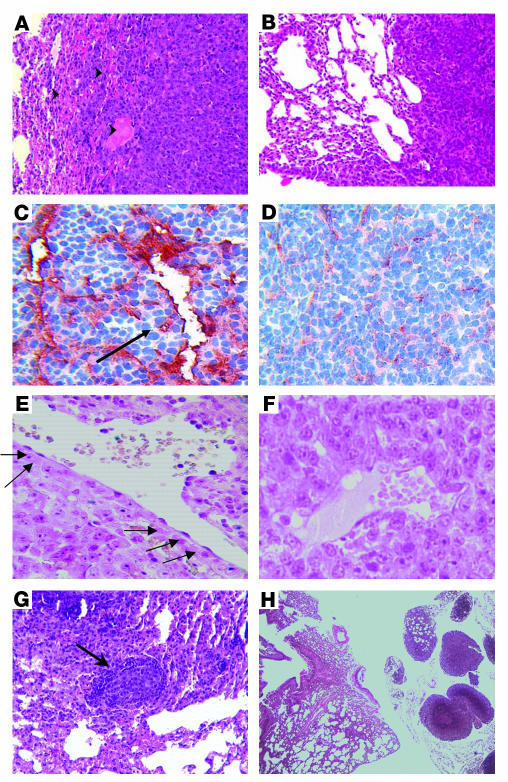
Figure 5.
Ad-PPE-Fas-c inhibits metastasis growth by antivascular action. Vascular impairment of tumor vessels in Ad-PPE-Fas-c–treated mice is shown. (A) H&E staining of a lung section taken from an Ad-PPE-Fas-c–treated mouse, showing hemorrhagic areas at the border between normal lung and metastasis. Arrowheads: hemorrhagic area. ×100. (B) H&E staining of a control, saline-treated mouse. ×100. (C) CD31 staining of tumor blood vessels in an Ad-PPE-Fas-c–treated mouse. Arrow: noncontinuous endothelial lining. ×200. (D) CD31 staining of an Ad-CMV-Fas-c–treated mouse. ×200. (E) TUNEL staining (marking apoptotic cells) of an Ad-PPE-Fas-c–treated mouse, showing apoptotic ECs in tumor blood vessels. Arrows: positive cells, stained with dark purple, lining a tumor blood vessel. ×400. (F) TUNEL staining of a control, Ad-PPE-luc–treated mouse, demonstrating unstained vessels. ×400. (G) Antitumor immune response. Micrometastases containing numerous apoptotic nuclei appear, surrounded by a mononuclear infiltrate, in this Ad-PPE-Fas-c–treated mouse. Arrow: mononuclear infiltrate. ×200. (H) Small metastases restricted to the perihilar region in an Ad-PPE-Fas-c–treated mouse. ×40.