Fig. 3.
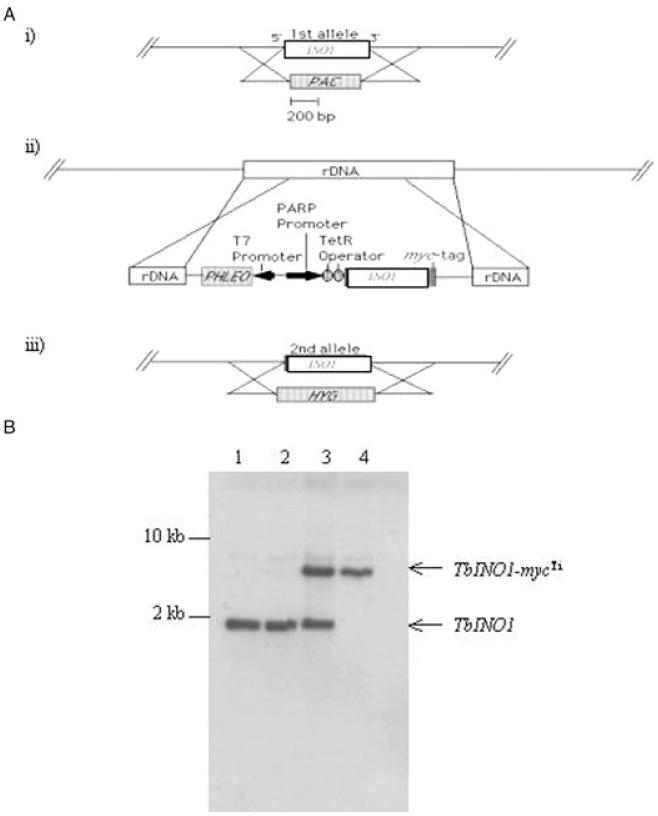
Construction of INO1 conditional double knockout cell line.
A. Schematic representation of construction strategy used. (i) One allele of INO1 was replaced by puromycin resistance gene (PAC) by homologous recombination generating ΔINO1::PAC cell line. (ii) A tetracycline-inducible ectopic copy of INO1 was introduced into the rDNA, generating INO1-mycTi ΔINO1::PAC cell line. (iii) While tetracycline induced the expression of the ectopic copy, the remaining allele was replaced by hygromycin resistance gene by homologous recombination, resulting in conditional double knockout cell line INO1-mycTi ΔINO1::PAC/ΔINO1::HYG.
B. Confirmation of genotype of T. brucei INO1 conditional double knockout cell line. Southern blot analysis of NcoI-digested genomic DNA (~2 μg) from wild-type T. brucei cells (lane 1), ΔINO1::PAC (lane 2), INO1-mycTi ΔINO1::PAC (lane 3) and INO1-mycTiINO1 ΔINO1::PAC/ΔINO1::HYG (lane 4); the INO1 ORF probe shows allelic TbINO1 at 1.9 kb and the ectopic copy TbINO1-mycTi at ~7 kb.