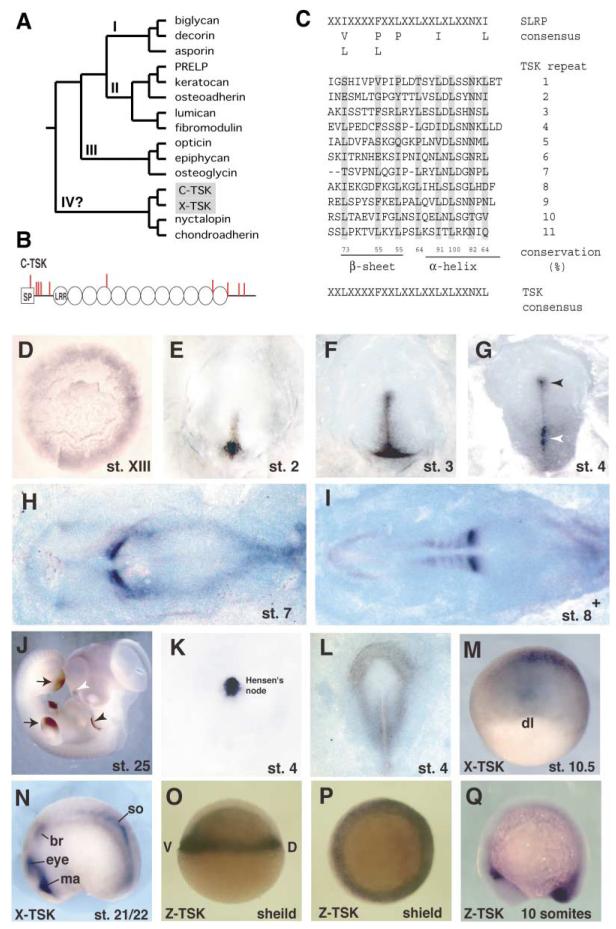
Figure 1. Primary Structure and Expression of TSK.
(A) Phylogenetic tree of the SLRP family. We used human protein sequences, C-TSK, and X-TSK in a Clustal W analysis.
(B) Schematic drawing of the primary structure of C-TSK. LRRs are indicated as circles. Cysteine residues are indicated as red bars. SP, signal peptide.
(C) 11 leucine-rich repeats have been aligned and yield a C-TSK consensus sequence (indicated at bottom). Conservation of leucines has been calculated (%).
(D–J) In situ hybridization with C-TSK.
(D) Stage XIII. The expression is detected mainly in the epiblast of the area opaca and weakly in the hypoblast.
(E) Stage 2. Expression in the newly formed primitive streak.
(F) Late stage 3. Expression in the primitive streak.
(G) Stage 4. Expression in the primitive streak (white arrowhead) and Hensen’s node (black arrowhead).
(H) Stage 7.
(I) 8+ embryos. Strong expression in the newly formed somites.
(J) Stage 25. Expression in wing and leg buds (black arrows), the edge of pharyngeal arch 2 (black arrowhead), and nasal pit (white arrowhead).
(K) Stage 4. Localized expression of chordin in Hensen’s node.
(L) Expression of BMP4 at stage 4.
(M and N) In situ hybridization with X-TSK at stage 10.5 (M) and stage 21/22 (N); br, branchial crest segment; ma, Mandibular crest segment; so, somite.
(O–Q) In situ hybridization with Z-TSK at shield stage (O, lateral view; P, anterior view) and 10 somite stage (Q, lateral view).