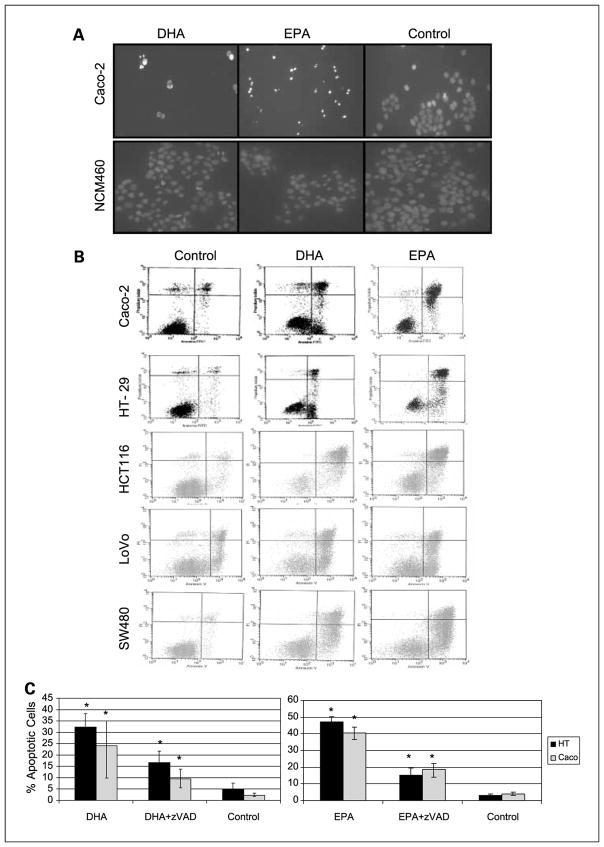
Fig. 1.
A, fluorescence microscopy images of 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole–stained Caco-2 and NCM460 cells 24 h postsupplement with DHA, EPA, or control. B, flow cytometry graphs representing propidium iodide concentration versus Annexin V concentration 24 h postsupplement in Caco-2, HT-29, HCT116, LoVo, and SW480 cells. Left to right, control cells, DHA, and EPA. The apoptotic population (right bottom quadrant) and/or late apoptotic population (right top quadrant) is always significantly higher in DHA and EPA-supplemented cells. C, quantification of apoptotic cells as % over total number of cells 24 h postsupplementation. Black bars, HT-29; gray bars, Caco-2. Left graph, the results for DHA; right graph, the results for EPA. *, statistical significance of P < 0.05. Differences are statistically significant in all cases after addition of broad-spectrum caspase inhibitor zVAD.