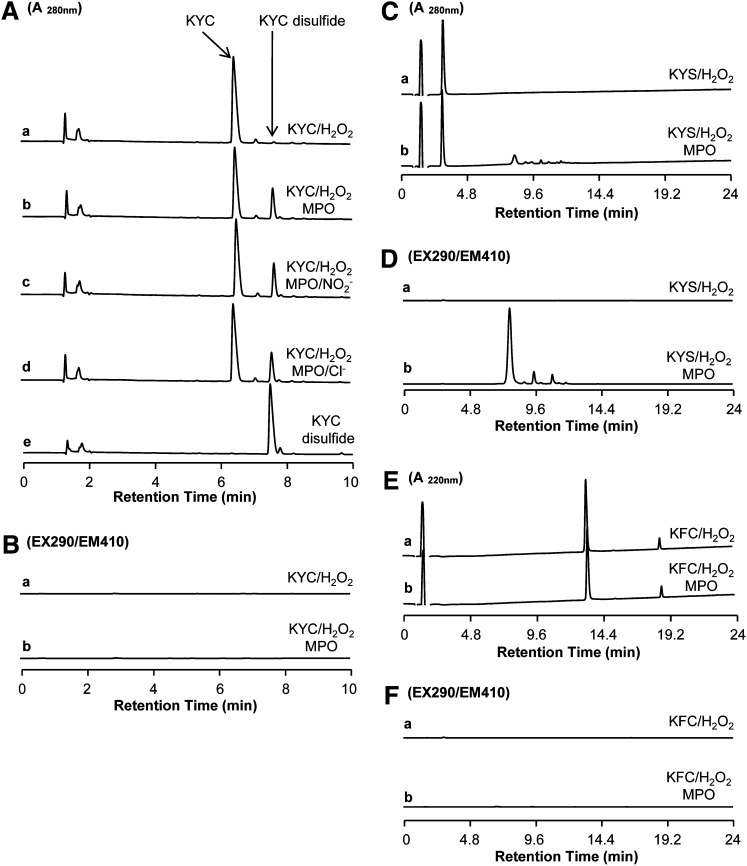
Fig. 2.
HPLC analysis of MPO-mediated KYC product formation. A: HPLC analysis of KYC products from various MPO-mediated oxidation reactions detected at 280 nm (A280). KYC (440 μM) was incubated with H2O2 (100 μM) in phosphate buffer (100 mM, pH 7.4) containing DTPA (100 μM) at room temperature for 30 min and the reaction products analyzed by HPLC (trace a). Reaction conditions and incubation times were the same as in trace a but with MPO included (50 nM) (trace b). Reaction conditions and incubation times were the same as in trace b but with NaNO2 (0.5 mM) included (trace c). Reaction conditions and incubation times were the same as in trace b but with NaCl (100 mM) included (trace d). HPLC trace of KYC disulfide standard (trace e). B: HPLC analysis of KYC products from MPO/H2O2-mediated oxidation detected by fluorescent detection at Ex = 290 nm (EX290) and Em = 410 nm (EM410). KYC/H2O2 (trace a) and MPO/KYC/H2O2 (trace b). C: HPLC analysis of KYS products from MPO/H2O2-mediated oxidation reactions detected at 280 nm (A280). KYS/H2O2 (trace a) and MPO/KYS/H2O2 (trace b). D: HPLC analysis of KYS products from MPO/H2O2-mediated oxidation reactions detected by fluorescent detection at Ex = 290 nm (EX290) and Em = 410 nm (EM410). KYS/H2O2 (trace a) and MPO/KYS/H2O2 (trace b). E: HPLC analysis of KFC products from MPO/H2O2-mediated oxidation reactions detected at 220 nm (A220). KFC/H2O2 (trace a) and MPO/KFC/H2O2 (trace b). F: HPLC analysis of KFC products from MPO/H2O2-mediated oxidation reactions detected by fluorescent detection at Ex = 290 nm (EX290) and Em = 410 nm (EM410). KFC/H2O2 (trace a) and MPO/KFC/H2O2 (trace b).