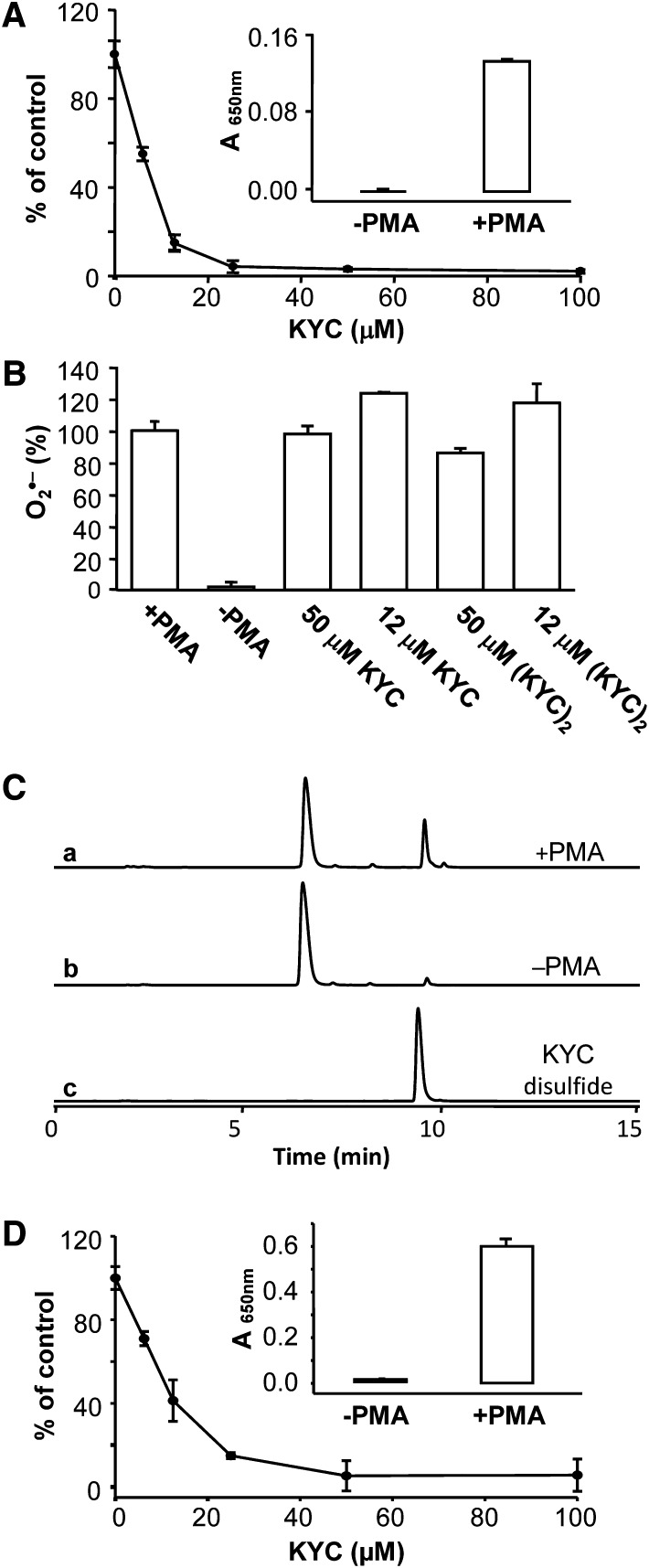
Fig. 4.
KYC specifically inhibits MPO in HL-60 cells and neutrophils. A: KYC inhibited HOCl formation. HL-60 cells (1.2 × 107/ml) were incubated with PMA and taurine as described in Materials and Methods. The reaction was stopped by catalase. After centrifugation, taurine chloramine was quantified by the KI/TMB assay. The inset panel shows that PMA is required to stimulate HL-60 cell HOCl production. Panel A shows that KYC dose dependently inhibits HL-60 cell HOCl production. B: Effects of KYC and KYC disulfide on HL-60 cells O2•− production. O2•− formation was analyzed by the superoxide dismutase-inhibitable cytochrome c reduction assay. HL-60 cells were incubated with cytochrome c (40 μM) with or without superoxide dismutase at 37°C for 10 min. The reaction was stopped by addition of catalase. After centrifugation, cytochrome c reduction was determined at 550 nm using a UV-Vis spectrophotometer. Results are expressed as percent of control, the data represents mean ± SD (n = 3). C: Effects of PMA on HL-60 cell-induced KYC product formation. HL-60 cells were stimulated with PMA (37°C for 30 min) and then incubated with KYC as above in panel (A). KYC oxidation products were analyzed by HPLC. Incubation with PMA-stimulated HL-60 cells (trace a). Incubation with nonstimulated HL-60 cells (trace b). KYC disulfide standard (trace c). D: Shows that KYC dose dependently inhibits HOCl production by PMA-stimulated neutrophils.