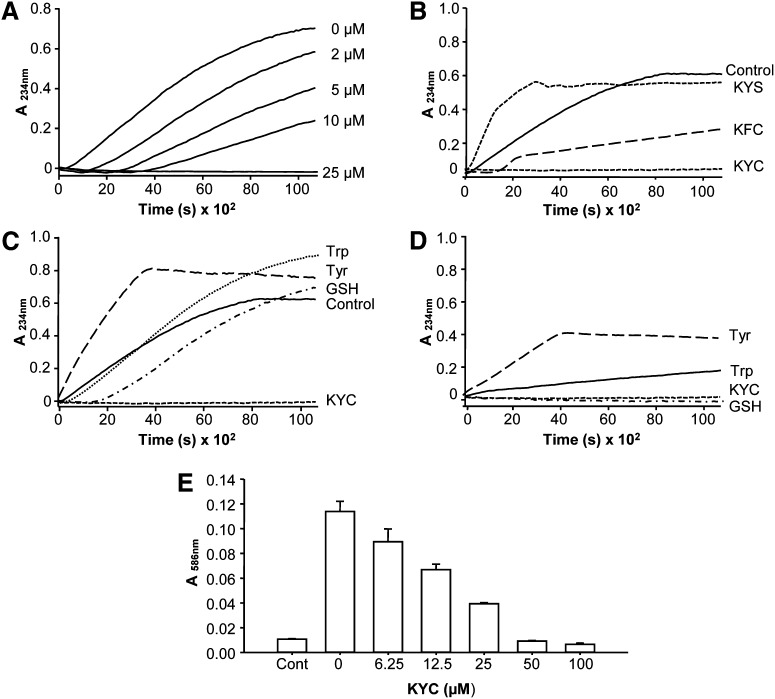
Fig. 6.
Effects of KYC on MPO-mediated LDL oxidation. LDL oxidation was induced by MPO (20 nM), H2O2 (100 μM), and NaNO2 (100 μM) in phosphate buffer (100 mM, pH 7.4) containing DTPA (100 μM) at room temperature. A: KYC dose-dependently inhibits LDL lipid oxidation induced by MPO/H2O2/NaNO2. Line graphs showing time- and concentration-dependent oxidation of LDL. KYC decreases MPO-mediated oxidation as measured by absorbance of conjugated dienes at 234 nm. B: Effects of 25 μM KYC, KYS, and KFC on MPO/H2O2/NaNO2-mediated LDL conjugated diene formation. C: Effects of KYC, GSH, Tyr, and Trp (25 μM) on MPO/H2O2/NaNO2-mediated LDL conjugated diene formation. D: Effects of KYC, GSH, Tyr, and Trp (25 μM) on MPO/H2O2-induced LDL conjugated diene formation. Incubation conditions were the same as above in (B) except without NaNO2 as outlined in Materials and Methods. E: MPO-mediated LDL MDA formation determined by N-methyl-2-phenylindole assay at 586 nm. The data represent three independent experiments.