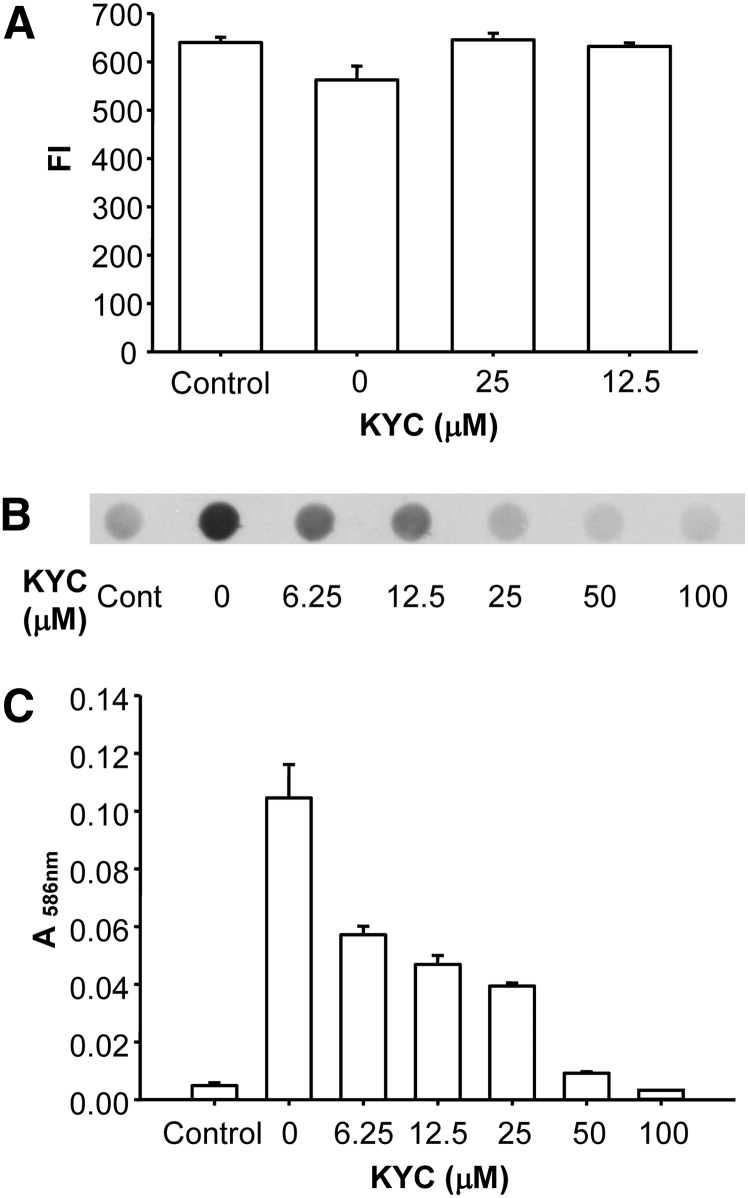
Fig. 8.
The effects of KYC on MPO-mediated lipoprotein oxidation, nitration, and chlorination. A: Inhibition of LDL Trp oxidation by KYC. LDL (0.15 mg/ml), NaNO2 (100 μM), H2O2 (100 μM), MPO (20 nM), and increasing concentrations of KYC in a phosphate buffer (100 mM, pH 7.4) containing DTPA (100 μM) were incubated at room temperature for 30 min. The oxidation of Trp in LDL was determined by measuring the changes of Trp fluorescence (Ex = 294 nm and Em = 345 nm). B: The effect of KYC on MPO-mediated Tyr nitration of LDL. LDL (0.5 mg/ml) was incubated with MPO (50 nM), H2O2 (50 μM), NaNO2 (50 μM), and increasing concentrations of KYC in phosphate buffer (100 mM, pH 7.4) containing DTPA (100 μM) at 37°C for 4 h. Reaction was stopped by addition of catalase (2,000 units/ml). The formation of NO2Tyr was assessed by dot blot analysis performed in triplicate for each condition. C: Effect of KYC on MPO-mediated lipid peroxidation of LDL induced by H2O2 and NaSCN. LDL (0.5 mg/ml) was incubated with MPO (50 nM), H2O2 (50 μM), NaSCN (250 μM), and increasing concentrations of KYC in phosphate buffer (100 mM, pH 7.4) containing DTPA (100 μM) at 37°C for 2 h. Reaction was stopped by catalase (2,000 units/ml). The lipid peroxidation was assessed by MDA assay performed in triplicate.