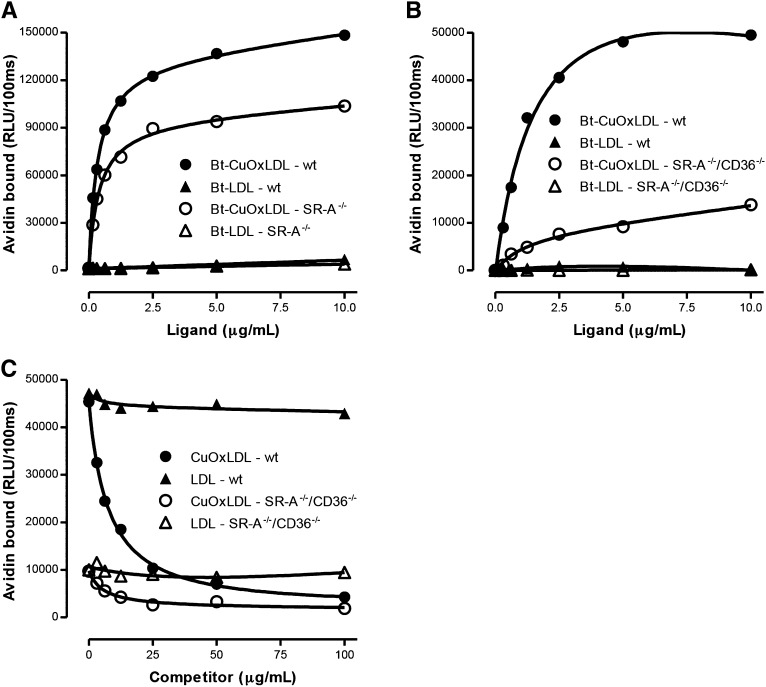
Fig. 2.
Binding of LDL and OxLDL to wt and scavenger receptor-deficient macrophages. A: Binding of Bt-OxLDL and Bt-LDL to thioglycollate-elicited peritoneal macrophages isolated from wt or SR-A−/− mice. Binding for each ligand was determined as described in the legend for Fig 1A. The apparent Kd for binding of CuOxLDL to wt macrophages was 0.42 ± 0.37 μg/ml and for binding to SR-A−/− macrophages was 0.46 ± 0.04 μg/ml. Maximal binding (Bmax) in ko macrophages was reduced ∼30% compared with wt. There was minimal binding of native LDL to wt or SR-A−/− macrophages. Data are representative of two experiments, with each point determined in triplicate. B: Specific binding of the same ligands to BMDM derived from Apoe−/− (wt) mice and from Cd36−/−/Sra−/−/ Apoe−/− triple ko mice (SR-A−/−/CD36−/−). Plating and culture of the BMDM and specific binding of CuOxLDL and LDL were performed as explained in the legend to Fig 1A. The apparent Kd for binding of CuOxLDL to Apoe−/− macrophages was 1.2 ± 0.2 μg/ml and to the triple ko macrophages was 3.5 ± 0.8 μg/ml. The Bmax to triple ko macrophages was reduced ∼80% compared with wt. Again, minimal binding of native LDL was noted to Apoe−/− or triple ko macrophages. Data are representative of two experiments, with each point determined in triplicate. Data for BMDM from Apoe−/− (wt) are the same as in Fig 1C. C: Competitive binding assay of Bt-CuOxLDL (2 μg/ml) to BMDM from Apoe−/− (wt) or Cd36−/−/Sra−/−/ Apoe−/− triple ko (SR-A−/−/CD36−/−) mice in the absence or presence of CuOxLDL or native LDL. Shown are the absolute levels of binding (in RLU/100 ms) for each ligand in the absence or presence of the indicated concentrations of competitors. The absolute binding of CuOxLDL to the triple ko macrophages is reduced about 80% compared with Apoe−/− macrophages. Unlabeled CuOxLDL was able to compete nearly all of the binding of Bt-CuOxLDL in Apoe−/− macrophages. In triple ko macrophages, unlabeled CuOxLDL was able to compete ∼75% of the residual Bt-CuOxLDL binding, consistent with the presence of other scavenger receptors capable of specific binding of OxLDL aside from CD36 and SR-A. Data are representative of two experiments, with each point determined in triplicate.