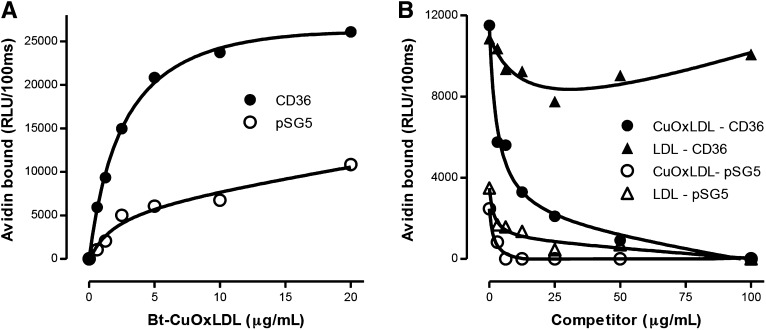
Fig. 3.
OxLDL specifically binds to COS-7 cells transfected with CD36. A: Binding of Bt-CuOxLDL to CD36 transfected cells. COS-7 cells were transfected with a plasmid containing CD36 (CD36) or empty plasmid (pSG5) as described in Materials and Methods. A total of 20,000 cells/well were plated in 96-well microtiter culture plates and cultured 48 h as described in Materials and Methods. Cells were washed and specific binding of Bt-CuOxLDL was determined as described in the legend of Fig 1A. B: Competitive binding assay of Bt-CuOxLDL (2 μg/ml) to mock-transfected COS-7 cells (pSG5) or to CD36 transfected cells (CD36) in the absence or presence of CuOxLDL or native LDL. Shown are the absolute levels of binding (in RLU/100 ms) for each ligand in the absence or presence of the indicated concentrations of competitors. The absolute levels of binding of Bt-CuOxLDL to mock-transfected cells was decreased ∼60–70% compared with CD36-transfected cells. Unlabeled CuOxLDL was able to fully compete binding to CD36-transfected cells and could compete the low level of binding to the mock-transfected cells, suggesting a low level of endogenous scavenger receptor activity in the COS-7 cells. In these experiments, there was a significant level of background alkaline phosphatase activity, and, as explained in Materials and Methods, Levamisole was added to block this activity. In both panels, the data shown are representative of three experiments, with each point determined in triplicate.