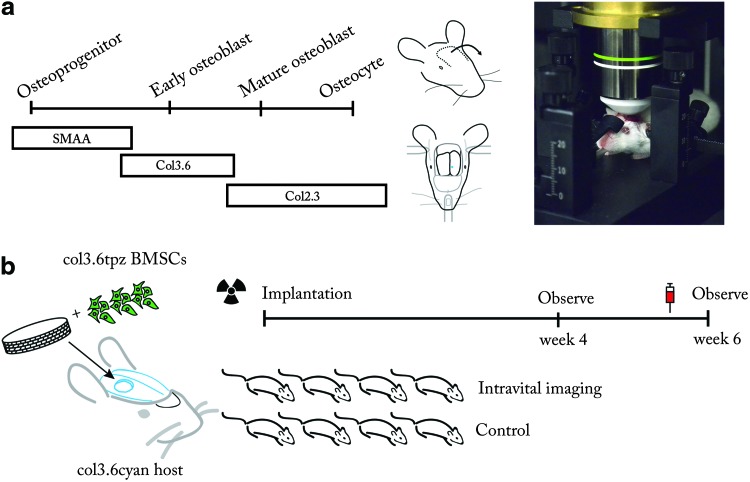
FIG. 1.
Examination of skeletal cells in native and tissue-engineered bone with live animal microscopy. (a) Reporters of the skeletal lineage used in this study, surgical procedure, and animal stabilization on the microscope. Left, skeletal lineage reporters used in this study. Middle, the calvarium was exposed by incision and the skin flap was sutured down. The stereotaxic frame stabilizes the head by three-point fixation at the ear canals and front teeth. Right, animal positioned under the objective lens of the two-photon microscope. (b) Observing tissue-engineered bone regeneration. Col3.6topaz bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs) were seeded onto a collagen-hydroxyapatite scaffold and implanted into a Col3.6cyan host. Host animals were irradiated and given a bone marrow transplant to prevent immunorejection of donor cells. At both 4 and 6 weeks later, animals in the imaging group were examined by two-photon microscopy. For comparison, the control group did not undergo imaging surgery. To visualize the mineral surface, Alizarin complexone was injected into both groups 1 day before sacrifice. Color images available online at www.liebertpub.com/tec