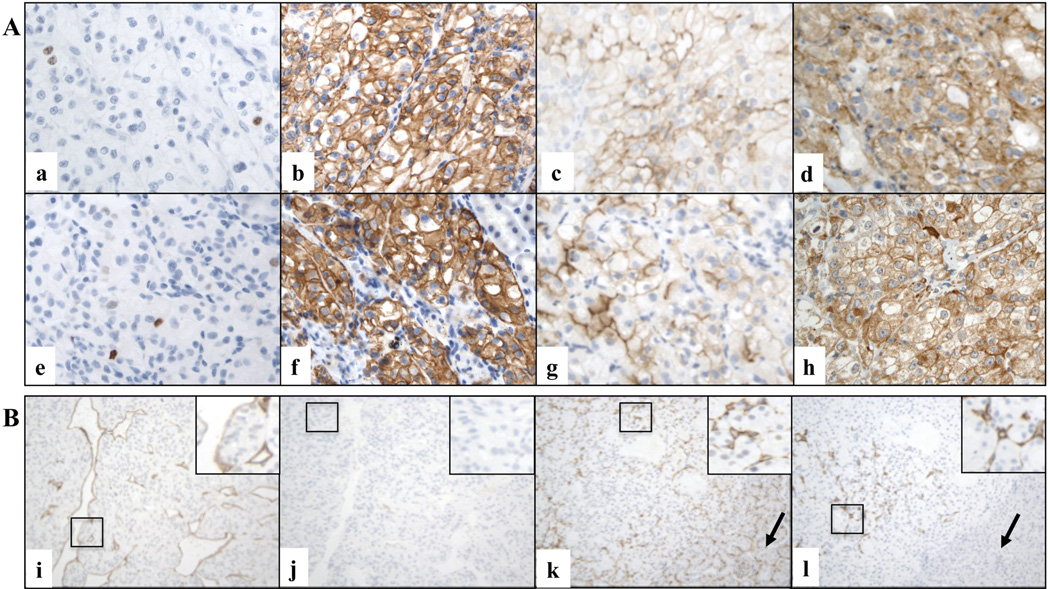
Figure 2. Immunophenotypic characteristics of RCC grafts.
A. Representative microscopic images of primary cRCC (a, b, c, d) and matched orthotopic xenograft (e, f, g, h) tissues immunostained for various markers (X600 magnification). Ki67 (a and e, case # 2), CAIX (b and f, case # 2), CD10 (c and g, case # 12), and VEGF (d and h, case # 6) stains are shown. B. Examples of species specific labeling of CD34-positive endothelial cells in two representative xenograft cases (X200 magnification). Murine (i) but not residual human (j) endothelial cells are detected in a FNG 4 cRCC graft grown in the host for 2 months (case # 19). Both murine (k) and human (l) endothelial cells are present in a FNG 3 cRCC graft grown in the host for 8 months (case # 9). Black arrows indicate the kidney of the mouse host.