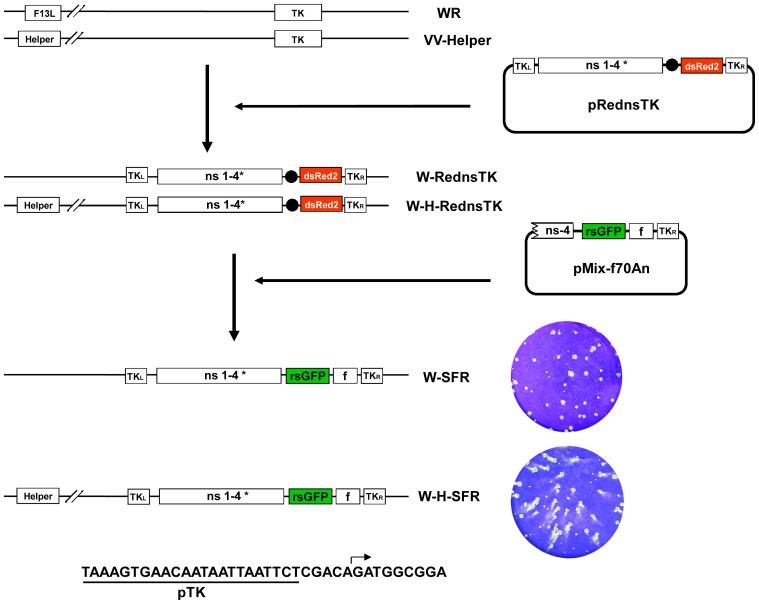
Figure 3. Construction of VV containing a SFV replicon.
Upper panel: Schematic representation of the virus genome, indicating the F13L and the TK loci. Viruses W-RednsTK and W-H-RednsTK were obtained by recombination of VV WR and VV-Helper, respectively, with plasmid pRednsTK. Viruses W-SFR and W-H-SFR were obtained by recombination of W-RednsTK and W-H-RednsTK, respectively, with plasmid pMix-f70An. Boxes labeled TKL and TKR denote the left and right recombination flanks or the TK gene. Boxes ns1–4* correspond to the genomic region coding the non-structural SFV proteins with an early VV transcription termination signal mutated. Black circle: VV synthetic early/late promoter. dsRed: red fluorescent protein gene. Helper: SFV genes for structural proteins, inserted downstream of the F13L gene under the control of a VV synthetic early/late promoter. rsGFP: green fluorescent protein gene. f: sequence from the 3′end of the SFV replicon, including 70 nucleotides adjacent to the PolyA and a 70 nt PolyA sequence. In the lower right, plaques formed by W-SFR or W-H-SFR on monolayers of BSC-1 cells for 48 hours. Below, sequence of the VV TK promoter and the predicted 5′ end of the SFV replicon (arrow).