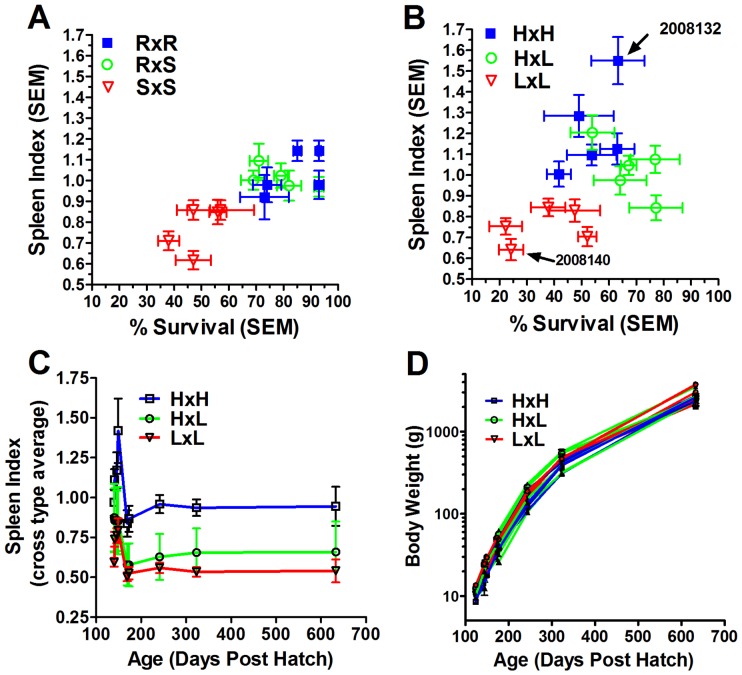
Figure 1. Family phenotypic correlation between naïve-animal spleen index (SI) and survival following challenge with F. psychrophilum.
(A) Trait correlation in fifteen 2007 year-class families selected based on BCWD resistance phenotype. Families were created using parents whose full-sibs were BCWD challenged in 2005 and identified as highly disease “resistant” (R) or “susceptible” (S) families. Five RxR (blue), RxS (green) and SxS (red) crosses were assayed for both survival (n = 200 fish per family, mean age 118 days,) and SI (n = 20 per family, mean age 128 days). (B) Trait correlation in 2008 year-class families. Fifteen families were created from fish whose full-sibs were evaluated in 2006 for SI and categorized as high SI (H) and low SI (L). Five HxH (blue), HxL (green) and LxL (red) crosses assayed for both survival (n = 120 fish per family, mean age 114 days,) and SI (n = 20 per family, mean age 145 days). (C) Stability of SI in HxH, HxL and LxL cross types. Values represent an average (±1 SEM) of 5 families per cross type. (D) Equivalent growth rates of the F1 SI QTL (2008) families.