Table 3. Significant and suggestive QTL for SI using half-sib family regression analysis1 in rainbow trout family 2008132.
| FChromWide | FExperWide | Closest marker10 | ||||||||
| Category | Omy2 | cM3 | LR4 | F- value5 | P = 0.05 6 | P = 0.05 7 |
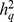 8
8
|
95% C.I.9 | Left | Right |
| Dam HS family | 1 | 5 | 10.76 | 11.09* | 7.12 | 13.64 | 0.07 | 0.0–27.0 | Ssa20_19NUIG | OMM1205 |
| 8 | 39 | 9.27 | 9.52* | 7.02 | 13.64 | 0.06 | 19.0–71.0 | OMM1579 | OMM1055 | |
| 13 | 25 | 7.46 | 7.63* | 6.63 | 13.64 | 0.05 | 0.0–60.0 | OMM1330a | OMY1UoG | |
| 18 | 70 | 6.47 | 6.59* | 6.36 | 13.64 | 0.04 | 2.0–70.0 | OMM1303 | OMM1352 | |
| 19 | 29 | 25.91 | 27.81** | 6.65 | 13.64 | 0.18 | 16.0–34.0 | OMM5216 | OMM5327 | |
| 26 | 1 | 10.78 | 11.12* | 5.97 | 13.64 | 0.07 | 0.0–22.0 | OMY1189b | OMM5231a | |
| Sire HS family | 1 | 30 | 8.01 | 8.02* | 5.97 | 12.28 | 0.05 | 4.0–45.0 | OMM1152 | OMM1355 |
| 2 | 10 | 6.54 | 6.67* | 4.93 | 12.28 | 0.04 | 4.0–81.0 | OMM1391a | OMM1131 | |
| 3 | 48 | 8.89 | 9.12* | 5.54 | 12.28 | 0.06 | 4.0–75.0 | OMM4025 | OMM1080 | |
| 5 | 57 | 25.31 | 27.12** | 6.08 | 12.28 | 0.18 | 29.0–80.0 | OMM1439 | OMM5213 | |
| 11 | 4 | 6.78 | 6.92* | 4.45 | 12.28 | 0.04 | 0.0–40.0 | OMM3093 | OMM1433 | |
| 16 | 0 | 12.33 | 12.77** | 4.62 | 12.28 | 0.09 | 0.0–42.0 | OMM1221 | OMYRGT6TUFa | |
| 17 | 10 | 7.17 | 7.32* | 6.07 | 12.28 | 0.05 | 0.0–58.0 | OMM1306 | OMM1607 | |
Half-sib regression interval mapping was performed with web-based software GridQTL [24].
The chromosome location with the highest estimated F-value was defined as the most likely QTL location. The map cM units are based on genetic maps developed for this QTL genome scan study.
The likelihood ratio test statistic was estimated as 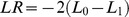 where L0 is the log likelihood of polygenic model and L1 is the log likelihood of the QTL model at the tested location (cM).
where L0 is the log likelihood of polygenic model and L1 is the log likelihood of the QTL model at the tested location (cM).
Asymptotically F-test statistic with the degrees of freedom(DF) being the number of sires or dams included for the numerator, and the total number of offspring minus twice the number of sires or dams for the denominator [25]. The QTL with F-value ≥ FChromWide P = 0.05 was defined as suggestive QTL (*) and QTL with F-value ≥ FExperWide P = 0.05 was defined as significant QTL (**).
Chromosome-wide F-value at P = 0.05 was estimated using 10,000 permutations with GridQTL [24].
Experiment-wide FExperWide P = 0.05 was estimated using 10,000 bootstraps with re-sampling with GridQTL [24].
The proportion of phenotypic variance explained by the QTL was calculated as 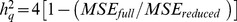 where MSEfull and MSEreduced are the mean squared error of the full and reduced model, respectively [25]. The estimated was corrected for selective genotyping according to Darvasi and Soller [61].
where MSEfull and MSEreduced are the mean squared error of the full and reduced model, respectively [25]. The estimated was corrected for selective genotyping according to Darvasi and Soller [61].
The 95% confidence intervals for each suggestive and significant QTL was determined using 10,000 bootstraps with re-sampling with software GridQTL [24].
The closest markers flanking (left and right) the chromosome location with the highest estimated F-value in the QTL scan.
