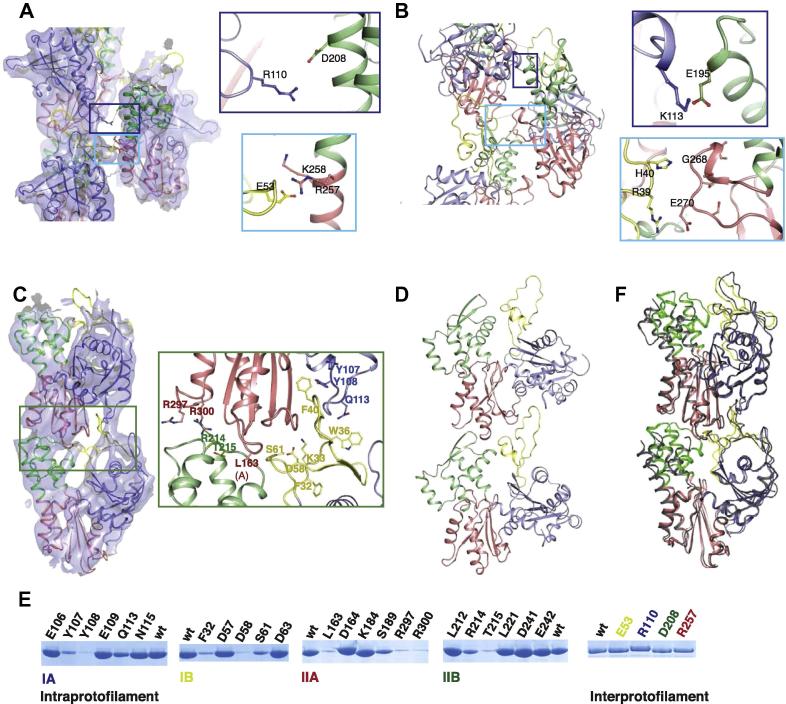
Fig. 5.
Filament interfaces of ParM and actin. (A) and (B) Inter-protofilament interfaces of ParM (PDB ID: 4A6J) (A) and actin (PDB ID 3MFP) (B). The regions of closest contact are shown in the insets. The corresponding regions in ParM and actin are shown in the same colour of outline for the insets. The cyan-outlined inset corresponds to the hydrophilic plug in actin. The polypeptides are coloured according to the domains. The cryoEM reconstruction of the ParM filament is also shown in surface representation. (C) and (D) Intra-protofilament interfaces of ParM (C) and actin (D). The residues shown to disrupt polymerisation upon mutation (refer (E)) are labelled in the inset for ParM. The cryoEM reconstruction of the ParM filament is also shown in surface representation. (E) Single point mutations at the protofilament interfaces of ParM disrupt polymerisation. Shown are the pellet fractions of the polymerisation assay (Materials and methods) of ParM mutants. All the residues shown have been mutated to alanine. Mutation to alanine of Y107, Y108 of domain IA, F32, D58, S61 of domain IB, L163, S189, R297, R300 of domain IIA, R214, T215 of domain IIB respectively affect polymerisation. (F) A superposition of the ParM-AMPPNP conformation (in grey) on the ParM filament structure (coloured according to the domains) shows that the domains are not optimally positioned to maintain the essential filament contacts.