Figure 6. Amino acid pari-wise similarity and substitution rates.
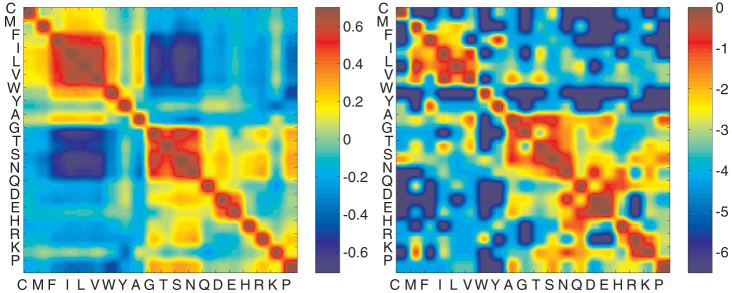
(Left A) Pair-wise similarity of amino acids, calculated from their energetic interactions (MJ matrix) and the average natural composition. There is a clear grouping of amino acids based on physical properties. Hydrophobic residues are most similar to each other, as are the hydrophilic residues. The similarity matrix, however, goes further and distinguishes residues based on charge. D and E are positively correlated because they are hydrophilic but also negatively charged. They are negatively correlated with residues K and R despite the same hydrophobicity measure, because K and R are charged positively. (Right B) PAM1 substitution matrix39. Entry (i,j) is the logarithm of the probability of amino acid i substituting amino acid j after an evolutionary distance of one accepted point mutation for every 100 amino acids. This matrix has a striking resemblance to the correlation matrix.
