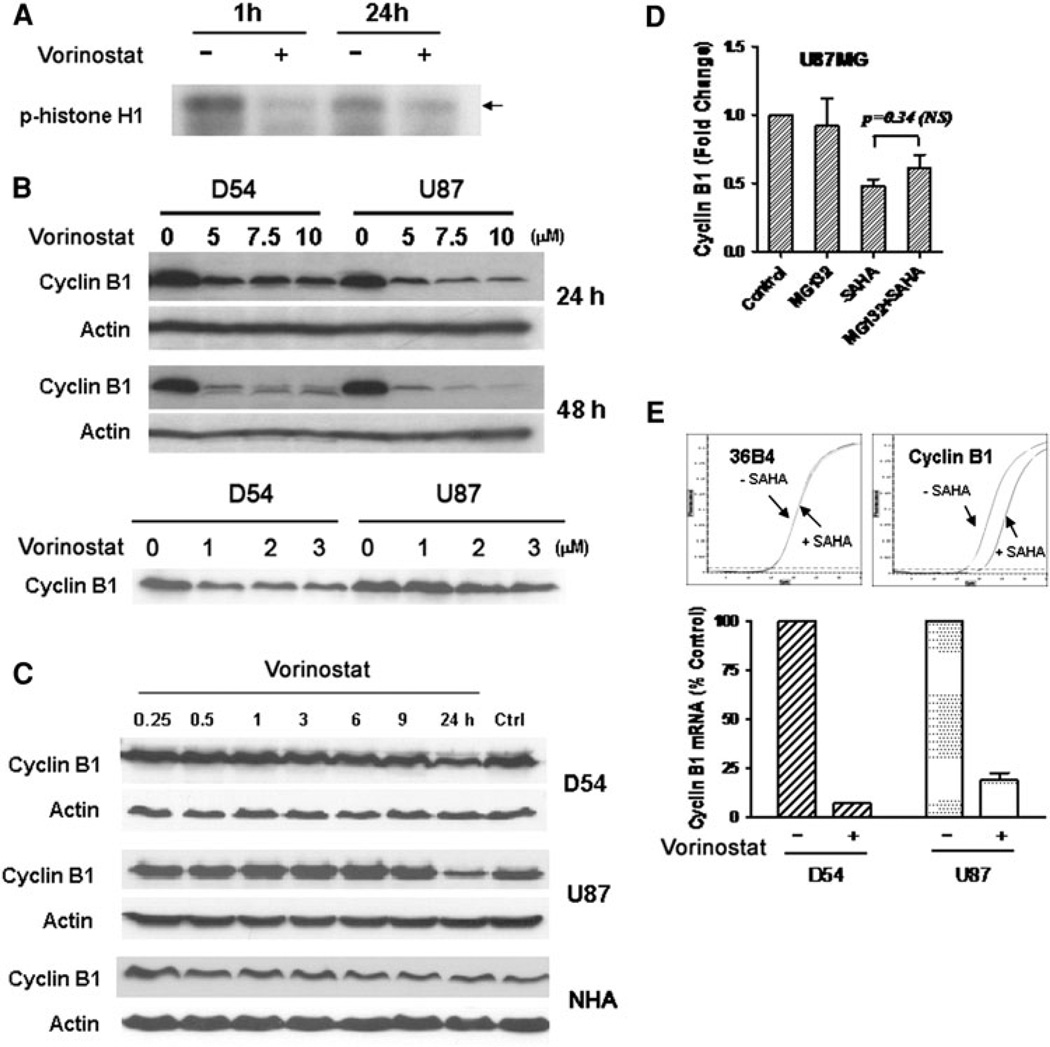
Fig. 5.
a Cells treated with vorinostat (3 µM) for the periods indicated were assessed for kinase activity of the cdk1/cyclin B1 complex in an in vitro kinase assay using histone H1 as a substrate. The cell lysates were subsequently subject to immunoblotting using an anti phospho-histone H1 antibody, b Cyclin B1 levels were determined in D54 and U87 cells after treatment with various doses of vorinostat at 24 and 48 h (higher concentrations, upper panel; lower concentrations, lower panel) (note the actin control for the upper panel blot is shared by that for the p21 in Fig. 3c). c D54, U87 and NHA cells were treated with vorinostat (3 µM) and the time course of changes in cyclin B1 levels were assessed by immunoblotting. d U87MG cells were treated with vorinostat alone (3 µM), MG132 alone, or MG132 followed by vorinostat. Levels of cyclin B1 were determined by immunoblotting and the intensity of the bands were quantitated and expressed relative to levels in untreated control. Statistical analysis was performed between vorinostat alone or vorinostat plus MG132 using a unpaired t-test with a two-tailed P value; significant values are ≤ 0.05). e Levels of cyclin B1 transcript in D54 and U87 cells were determined by quantitative real-time PCR (upper panel) after treatment with vorinostat (3 µM) and with transcript levels of the ribosomal protein 36B4 as a control. Mean CT levels of cyclin B1 transcript (lower panel) are shown relative to levels of 36B4 transcript