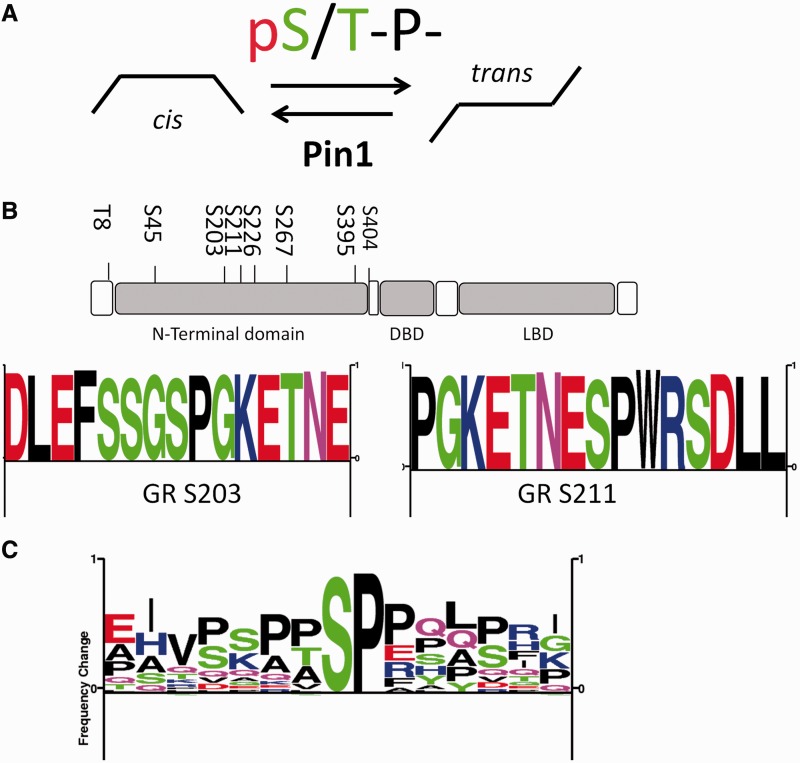
Figure 1.
Proline-directed phosphorylation sites in the GR. (A) Pin1 sites binds to pS/T-P sites [e.g. WFYpSPR (8)]; cis/trans isomerization at pS/T-proline sites is reduced by phosphorylation (7), but is then a target for Pin1, which catalyzes cis/trans isomerization at pS/T-P motifs. (B) The major phosphosites found in the N-terminal region of GR (28). The majority of phosphosites in GR are proline-directed S/T-P sites. Some of these sites have been shown to be required for transactivation (S203 and S211), whereas some have shown to have a negative effect on GR activation (S226 and S404). Eight of the major proline-directed GR sites were used to create the sequence logo (28). (C) Pin1 recognition sites [taken from (28) previously found in nuclear receptors: androgen receptor (18) estrogen receptor (19), PPARγ (21), PML (29) and Nur77(TR3 (30,31)] were used to generate a sequence frequency logo (28).