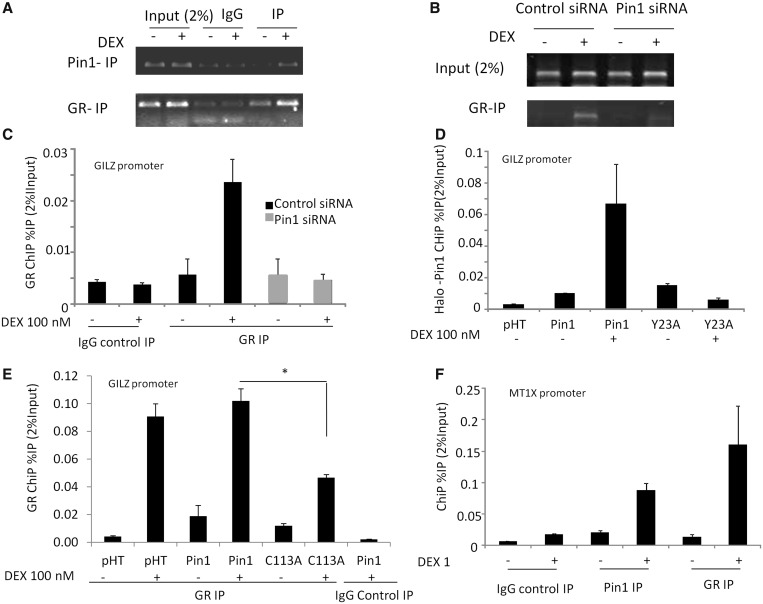
Figure 6.
The effect of Pin1 on GR recruitment to the GILZ promoter. A549 cells were stimulated with 100 nM DEX for 1 h and chromatin prepared as described in the ‘Materials and Methods’ section, ChIP was carried out using an anti-Pin1 (A) or anti-GR antibody (B) and PCR primers for the GILZ promoter (n = 6). (C) A549cells were transfected for 48 h with control or Pin1 siRNA, following a 1 h DEX treatment, ChIP was carried out with an anti-GR antibody and PCR primers for the GILZ promoter. (D) Halo-ChIP was carried out with Halo- Control protein (pHT), Halo-Pin1 or a WW-domain mutant Pin1 (Y23A). A549 cells were transfected with each Halo tag protein for 16 h and then treated with DEX (100 nM) for 1 h before cross-linking and binding to the Halo-link resin. Pin1 loading on the GILZ promoter was determined using qPCR Results are expressed as percentage immunoprecipitaion from 2% of the input chromatin [%IP (2% input)]. (E) A549 cells were transfected for 16 h with control pHT, pHT-Pin1 or pHT-Pin1 C113A inactive mutant, following a 1 h DEX treatment, ChIP was carried out with an anti-GR antibody and PCR primers for the GILZ promoter (as described earlier in the text). (F) ChIP was carried out using as described earlier in the text using an anti-Pin1 or anti-GR antibody and PCR primers for the MT1X promoter. Statistical analysis was determined using a one-way ANOVA and a Bonferroni post-hoc test (P < 0.05*).