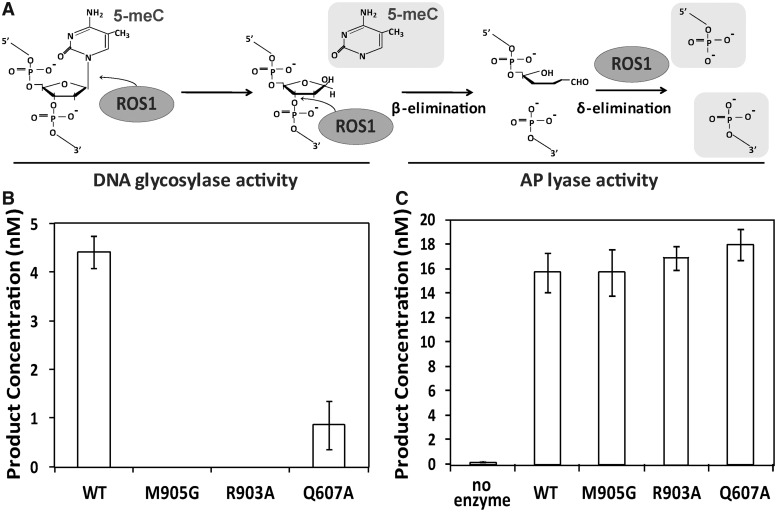
Figure 3.
Q607A, M905G and R903A mutant proteins lack DNA glycosylase activity on 5-meC:G pairs but retain AP liase activity. (A) Schematic diagram of ROS1 DNA glycosylase/AP lyase activity on 5-meC. ROS1 excises 5-meC as a free base and then cleaves the phosphodiester backbone at the 5-meC removal site by successive β,δ-elimination. (B) DNA glycosylase assay. The generation of incision products was measured by incubating purified WT ROS1 or mutant variants (20 nM) at 30°C for 4 h with a double-stranded oligonucleotide substrate (20 nM) containing a single 5-meC:G pair. After incubation, NaOH (100 nM) was added and samples were immediately transferred to 90°C for 10 min. Products were separated in a 12% denaturing polyacrylamide gel and the amounts of incised oligonucleotide were quantified by fluorescent scanning. (C) AP liase assay. A double-stranded oligonucleotide substrate containing an AP site opposite G (20 nM) was incubated at 30°C for 2 h in the presence of purified WT ROS1 or mutant variants (20 nM). Samples were treated with NaBH4 (300 mM) at 0°C for 30 min to stabilize nonprocessed AP sites and neutralized with 100 mM Tris–HCl, pH 7.4. Products were separated in a 12% denaturing polyacrylamide gel and the amount of incised oligonucleotide was quantified by fluorescent scanning. Values are mean ± SE (error bars) from three independent experiments.