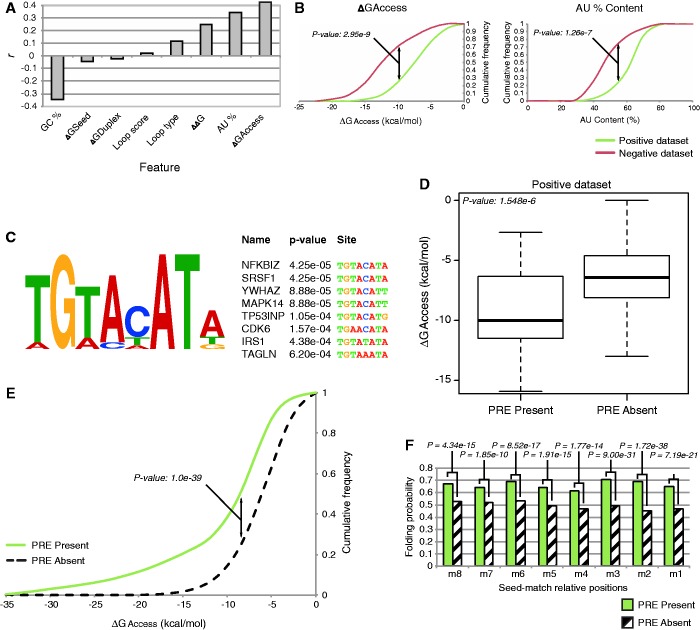
Figure 1.
PRE is enriched in validated and predicted thermodinamically inaccessible regions. (A) Correlation of different features to miRNA binding effectiveness measured on the training dataset. Local target accessibility (ΔGaccess) and AU content exhibit the greatest correlation. (B) Cumulative frequency plots show that functional targets (positive data set) are more likely to reside within 3′-UTR regions with a higher AU content, and that there is higher target accessibility with respect to non-functional targets (negative data set). P-values are given by Welch’s t-test. (C) Motif discovery analysis performed using MEME shows an enrichment for the PRE motif belonging to the Pumilio family proteins (e-value: 1.2e-22). Top enriched mRNA bearing PRE motifs are shown. (D) Presence of the PRE motif well stratifies the functional interactions between highly accessible and poorly accessible targets. The P-value is given by Welch’s t-test. (E) Cumulative frequency plot of top 20 PRE-associated human miRNA families. Seed-matches with nearby PRE motifs are enriched within poorly accessible regions with respect to those lacking a close PRE. The P-value is given by the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. (F) The base probability of the seed-match positions for the top 20 PRE-associated miRNA families in human. Sites with nearby PRE motifs exhibit a higher probability of being already engaged in a bond within the local 3′-UTR secondary structure. Positions m8 to m1 are paired, respectively, to miRNA’s seed positions 1–8. P-values per base are given by a Chi-Squared test.