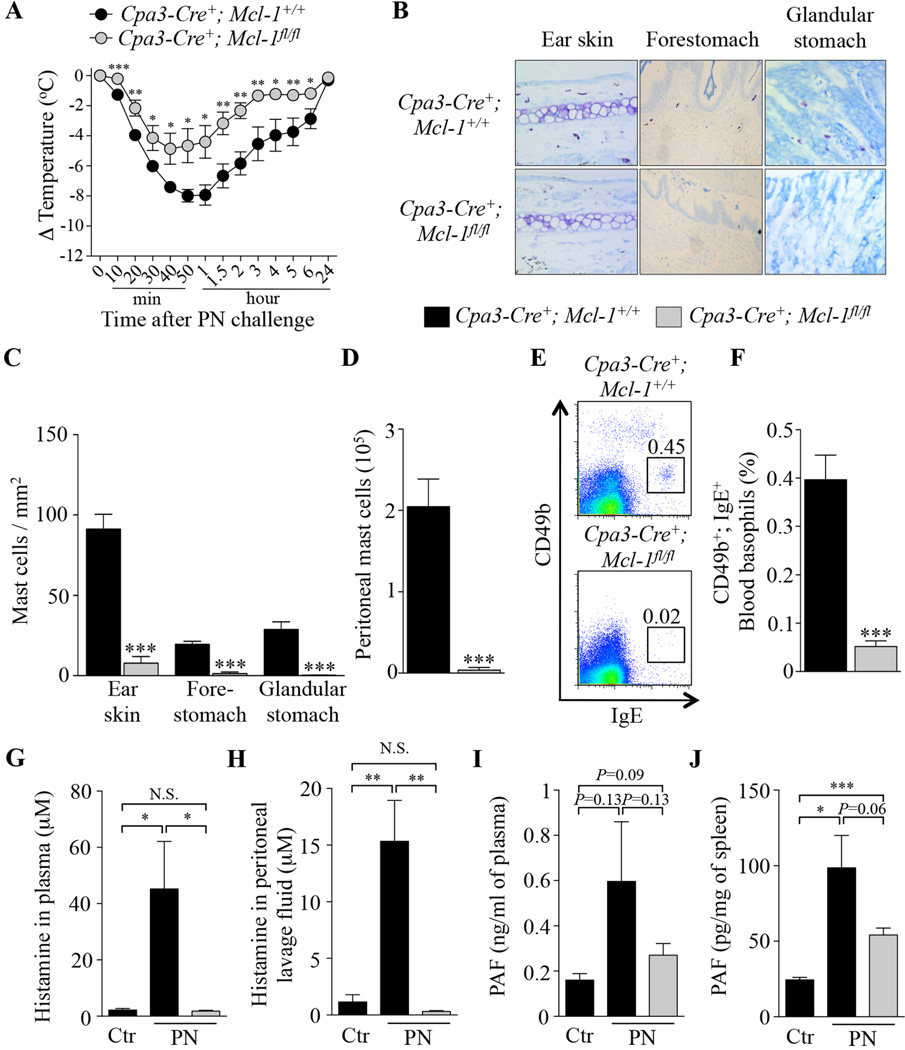
FIG 5. Peanut-induced anaphylaxis in Cpa3-Cre+; Mcl-1fl/fl mast cell- and basophil-deficient mice.
(A) PN-induced hypothermia in PN-sensitized Cpa3-Cre+; Mcl-1+/+(n=6) and Cpa3-Cre+; Mcl-1fl/fl (n=7) mice. (B–C) Toluidine blue staining for MCs (B) and numbers of MCs (C) in sections of ear skin, forestomach and glandular stomach. (D) Numbers of MCs in the peritoneal lavage fluid. (E–F) Representative flow cytometry plots (E) and percentage (F) of blood basophils (CD49b+; IgE+). (G–J) Mice were sensitized with cholera toxin (CT) and PN (PN; n=5–7) or CT only for control mice (Ctr; n=3–4), and sacrificed 20 min after challenge with PN to measure levels of histamine and PAF. (G–H) levels of histamine in plasma (G) and peritoneal lavage fluid (H). (I–J) levels of PAF in plasma (I) and spleen samples (J). Data are mean ± SEM or mean + SEM; *, ** or *** = P < 0.05, 0.01 or 0.001 vs. corresponding control group.