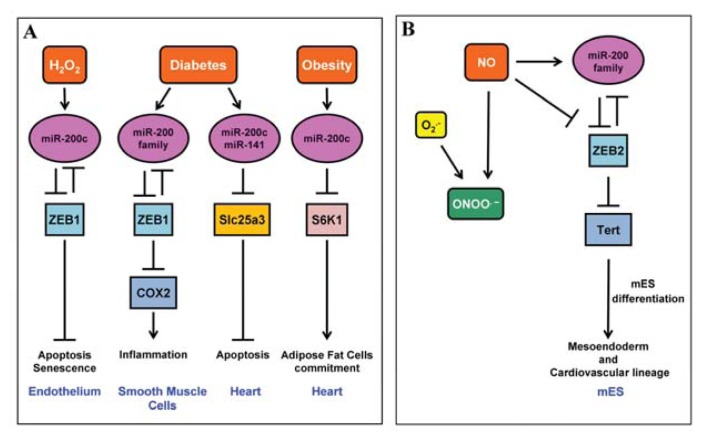
Figure 2.
(A) miR-200 family role in endothelial dysfunction and in cardiovascular complications linked to diabetes and obesity. This picture summarizes different pathways where a source of ROS or a pathology associated to elevated ROS production (coloured in red) plays a causal role in endothelial or cardiovascular diseases. The tissue or organ district where these mechanisms have been identified are coloured in blue; (B) miR-200 family and NO. Schematic representation of the role played by the free radical NO on miR-200 family induction which leads to ZEB2 downmodulation and Tert upregulation, inducing mES differentiation towards the mesendoderm and cardiovascular lineage.