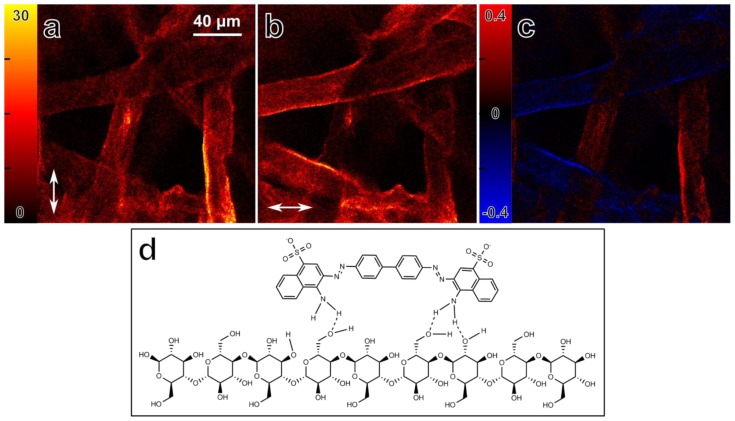
Figure 7.
Fluorescence detected nonlinear absorption anisotropy of Congo Red molecules bound to a filter paper (cellulose). (a,b) Fluorescence intensity images, obtained simultaneously with different laser polarizations. The arrows indicate the polarization direction; (c) Image of fluorescence detected absorption anisotropy, defined as r = (IV − IH) / (IV + IH)max. Maximum absorption anisotropy occurs when one of the polarizations is parallel to the cellulose fibers; (d) Binding of Congo Red (top) to a cellulose molecule. Due to the symmetry of the Congo Red molecule, and many possible hydrogen bonding sites between cellulose and Congo Red, the diphenol backbone of the Congo Red molecule is likely to be parallel to the cellulose fiber orientation. Possible hydrogen bonds are indicated with dashed lines.