Table 2. Model parameters.
| Parameter | Value |
| Time step | 1 week |
| Simulation time | 2000 centuries |
| Host parameters | |
Maximal population size 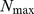
|
4980 individuals |
| MHC diversity | 1 locus with 14 alleles |
| Number of KIR loci | 5 |
| Bit string length | 16 bitsa |
Specificity 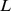 (bit scale) (bit scale) |
1–10 bits |
Host mutation rate 
|
0.00005 per allele per birth event |
| Infection b | |
Infection state 
|
0 (susceptible), 1 (acute), 2 (chronic) |
Probability of viral transmission during acute phase 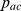
|
0.85 per contact |
Probability of viral transmission during chronic phase 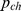
|
0.15 per contact |
Probability of clearing the wild-type virus 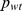
|
0.85 |
Probability of clearing the MHC downregulating virus 
|
0.75 |
Probability of clearing the virus evolving decoy molecules 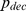
|
0 |
Immunity time 
|
10 years |
Acute infection time 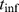
|
4 weeks |
| Virus parameters | |
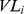
|
0 (for 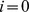 ), 0.1 (for ), 0.1 (for 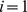 ), 0.06 (for ), 0.06 (for 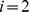 ) ) |
Virus mutation rate 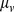
|
0.0001 per week |
| Initial conditions | |
Initial population size 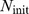
|
4500 individuals |
| KIR initial diversity (SRI) | 5 (1 allele per locus) |
: The choice to use 16-bit strings represents a large enough theoretical repertoire of 65,536 sequences.
: The parameters used for the infection are chosen to maintain the epidemic. Changing the length of the acute phase or the probabilites of clearance do not affect our results on the evolution of the KIRs qualitively (results not shown).
