Figure 1. Natural mechanisms for female host-seeking inhibition after a blood meal.
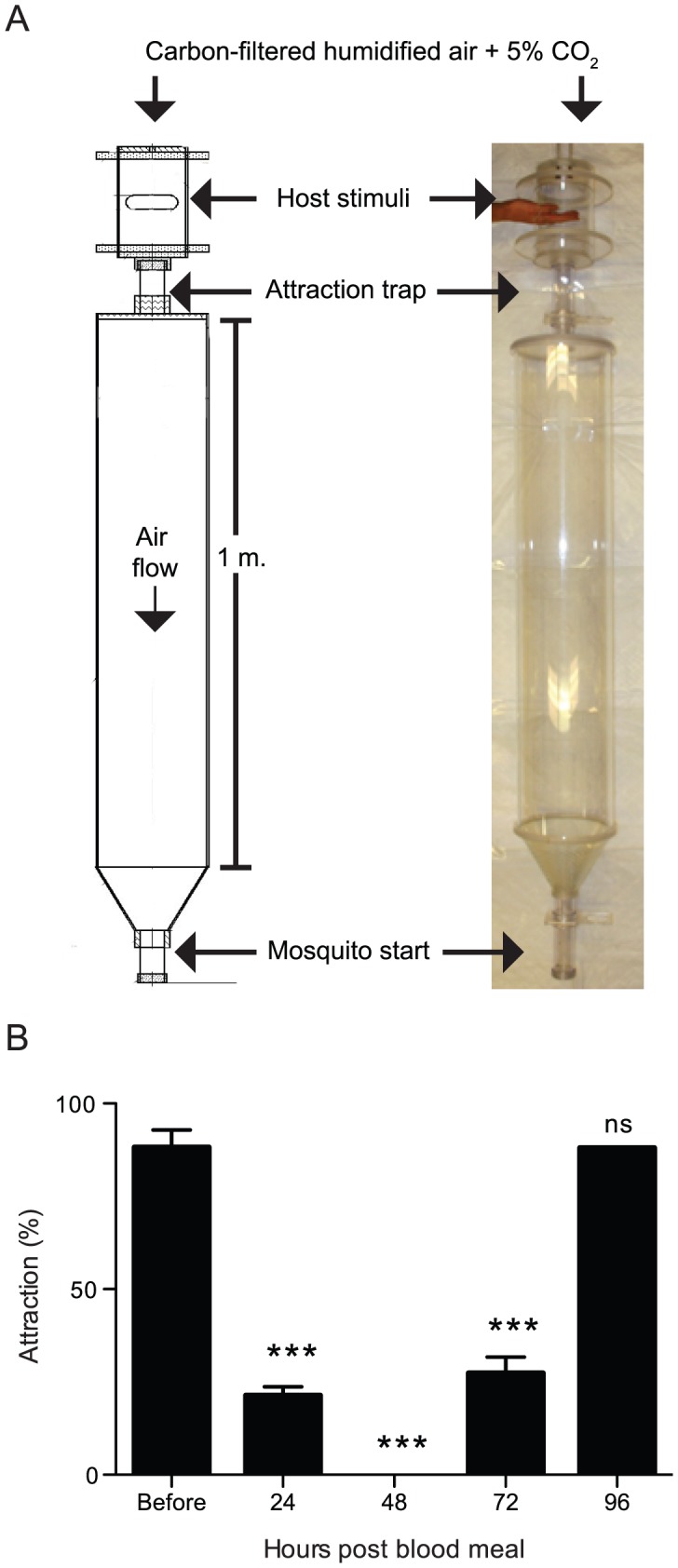
(A) Diagram (left) and photograph (right) of the uniport olfactometer with a human hand presented as stimulus. (B) Attraction of female Ae. aegypti to a human host throughout the gonotrophic cycle (n = 3–5; ∼20 females per trial). Access to egg laying locations was permitted after 72 hours and observed at 96 hours. Data are plotted as mean±standard error of the mean (SEM). ANOVA with Dunnett's Correction for Multiple Comparison; *** = p<0.001, ns = not significant.
