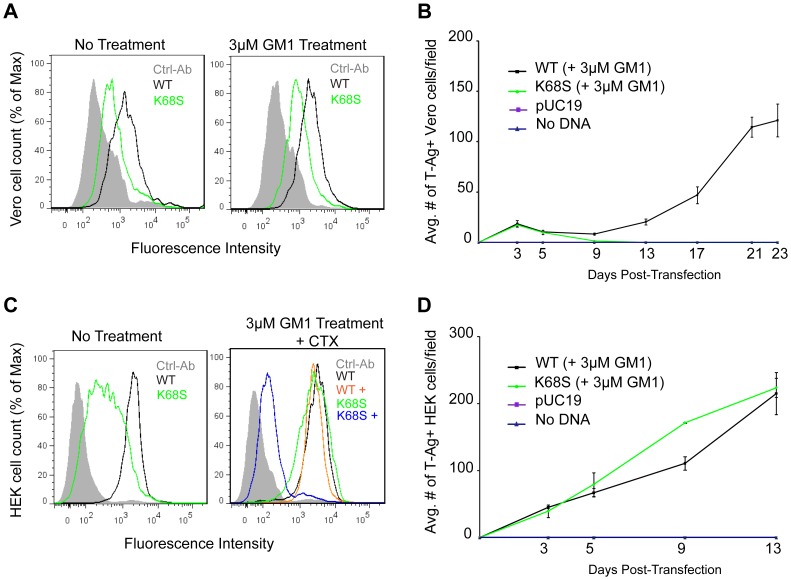
Figure 6. K68S BKPyV uses NeuAc-GM1 as a receptor for attachment and infection.
(A) Binding of BKPyV K68S to Vero cells. Cells were treated as in 3C fixed and pentamer binding to cells untreated (left) or treated with NeuNAc-GM1 (right) assessed by flow cytometry. Histograms show the fluorescence intensity of the Alexa 488 antibody alone (gray-filled), WT pentamer (black) and K68S pentamer (green) for 1×104 events. (B) Growth assay for BKPyV K68S in Vero cells. Cells were transfected as previously described, treated with NeuNAc-GM1, fixed and stained over 23 days. Viral spread was quantified by scoring for cells expressing T-Ag. The anti-V antigen monoclonal antibody 597 used in Figures 1 and 3 recognizes an epitope that is disrupted by the K68S mutation, requiring the use of an mAb against T-Ag. The average number of T-Ag positive cells is plotted from 3 independent experiments. (C) Binding of BKPyV K68S to HEK cells. Cells were treated as previously described, fixed and pentamer binding to cells untreated (left), or treated with NeuNAc-GM1 and CTX (right) assessed by flow cytometry. Histograms show the fluorescence intensity of the Alexa 488 antibody alone (gray-filled), K68S pentamer (green) WT pentamer (black), WT pentamer with CTX (orange) and K68S pentamer with CTX (blue) for 1×104 events. (D) Growth assay for BKPyV K68S in HEK cells. Cells were transfected as previously described, treated with NeuNAc-GM1, fixed and stained over 13 days. Viral spread was quantified as above. Gangliosides were added every 3 days.